
05-09 May 25
Convention Center - Auditorium della Tecnica,
Rome, Italy
Statements
- Home /
- About us /
- Events /
- GEO Global Forum 2025 /
- Statements
Statement Type
Loading...
Member Type
Loading...

Committee on Earth Observation Satellites

European Association of Remote Sensing Companies
Full Statement





“EARSC firmly believes that a successful partnership between governments, academia, and the private sector is essential for realising the SDGs. EARSC active participation in GEO as a participating organization since 2016 and EuroGEO has significantly heightened the interest of European Earth Observation companies in GEO, demonstrating the pivotal role such collaborations play in advancing our shared goals”

Emmanuel PajotEARSC Secretary General

“As the Chair of EARSC, I find it crucial to engage in ongoing discussions with organizations like GEO and its members. EARSC is a valuable asset, representing and advocating for the European EO services industry's perspective.

Marc Tondriaux EARSC chairman representing the Board of Directors

“The EU Copernicus programme is a key asset contributing to GEO. Through its involvement in EuroGEO, EARSC is supporting the engagement of the private sector in GEO and is leading activities to strengthen connections between all actors, policy makers, researchers and companies, actively supporting the GEO Work programme”
“EARSC is the single voice representing the European EO Services industry addressing overseas export markets as well as new customer segments. EARSC brings companies into GEO activities and provides valuable inputs through GEO activities. EXPANDEO, the EARSC annual gathering is an excellent platform for networking”
“The EARSC Awards are not just a recognition of excellence but voice to showcase the transformative power of innovation in Earth observation and EXPANDEO is a great platform for pushing the boundaries of what's possible in our quest to understand and protect our planet”
“EARSC is committed to highlighting the significant value delivered by EO data and services to citizens, corporations and governments. EARSC actively stimulates the uptake of services based on satellite data, to bring the benefits of space to society”

EARSC secretariat


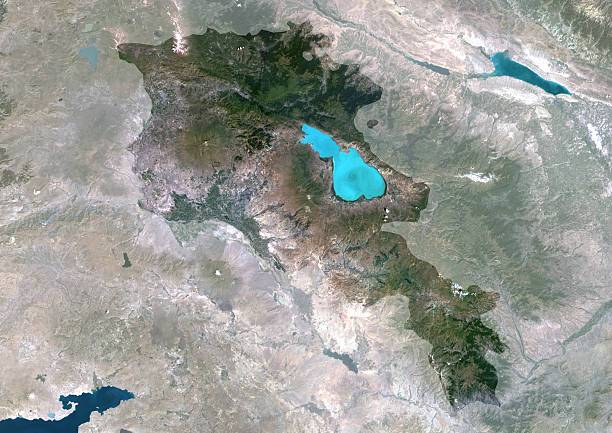
Armenia
“The Republic of Armenia places great significance on the development of its national Space and Earth Observation related capacities and science, with a special focus on Earth observation, which becomes and still remains one of the most impactful and dynamically growing sub-sector since 2020”

Shushanik AsmaryanCorrespondence Contact to make official submissions to the GEO Secretariat on behalf of GEO Principal of Armenia
October 13-19, 2024, Milan, Italy
Armenia’s Earth Observation capacities were prominently showcased at the exhibition of the 5th World Astronautical Congress. During the event, initial negotiations began between the Center for Ecological-Noosphere Studies (CENS) of the National Academy of Sciences of Armenia and the Mohammed Bin Rashid Space Centre (MBRSC) Laboratory at the University of Dubai, United Arab Emirates.

Shushanik AsmaryanCorrespondence Contact to make official submissions to the GEO Secretariat on behalf of GEO Principal of Armenia Deputy Director for Science/Head of GIS and Remote Sensing Department Center for Ecological-Noosphere Studies NAS Armenia

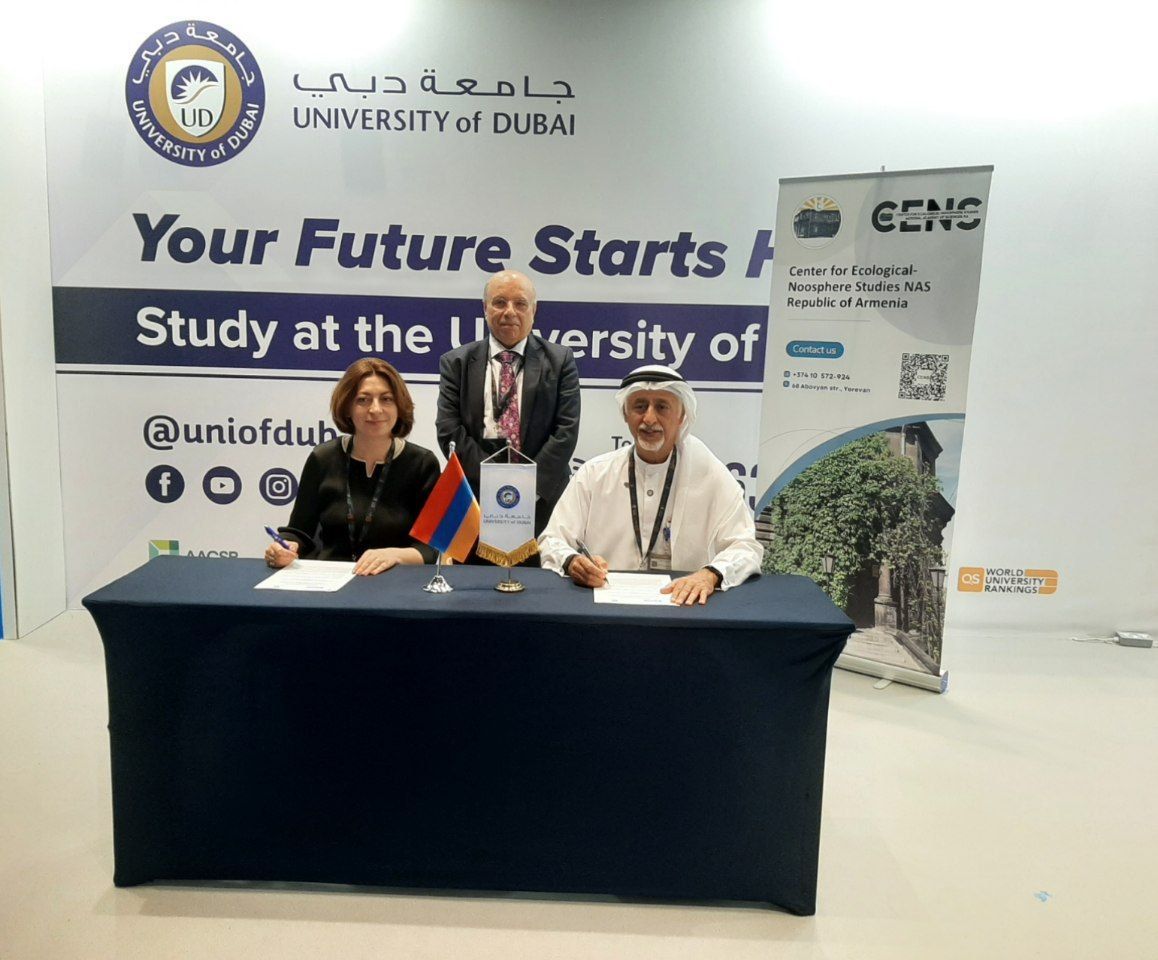
8 April, 2025, Dubai, AUE
A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was successfully signed between the Center for Ecological-Noosphere Studies (CENS) and the University of Dubai during the ISPRS Geospatial Week 2025. Under this agreement, joint initiatives are planned in the fields of environmental sciences, sustainable development, and ecological innovation, with a particular focus on the integration and application of satellite remote sensing technologies in research and decision-making processes.

Shushanik AsmaryanCorrespondence Contact to make official submissions to the GEO Secretariat on behalf of GEO Principal of Armenia Deputy Director for Science/Head of GIS and Remote Sensing Department Center for Ecological-Noosphere Studies NAS Armenia

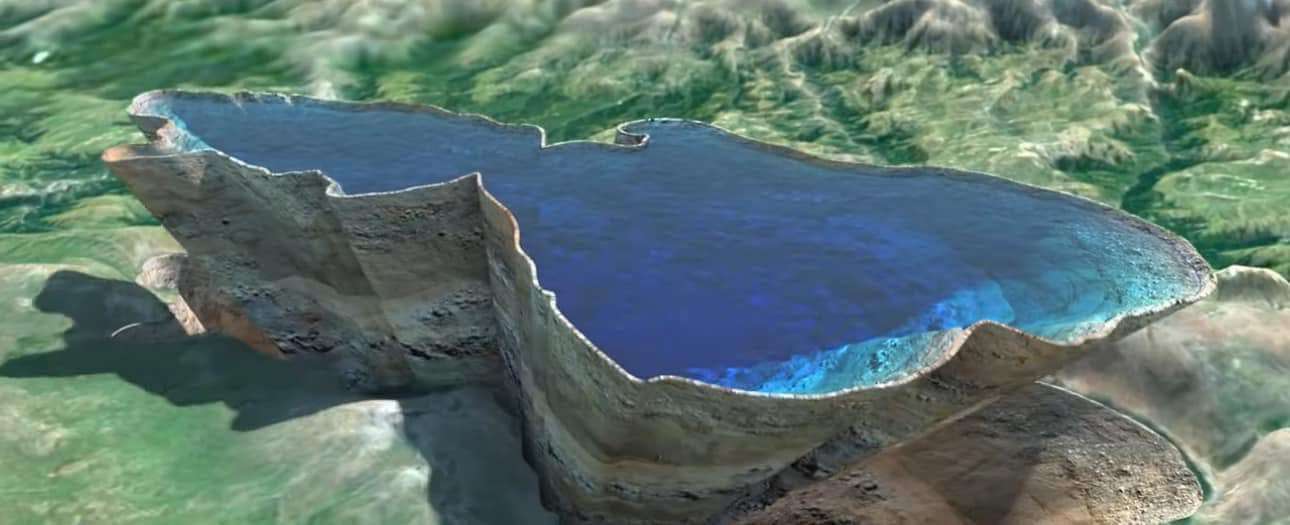
Satellite Earth observation has been integrated into the newly updated monitoring system of Lake Sevan in Armenia.

Shushanik AsmaryanCorrespondence Contact to make official submissions to the GEO Secretariat on behalf of GEO Principal of Armenia Deputy Director for Science/Head of GIS and Remote Sensing Department Center for Ecological-Noosphere Studies NAS Armenia

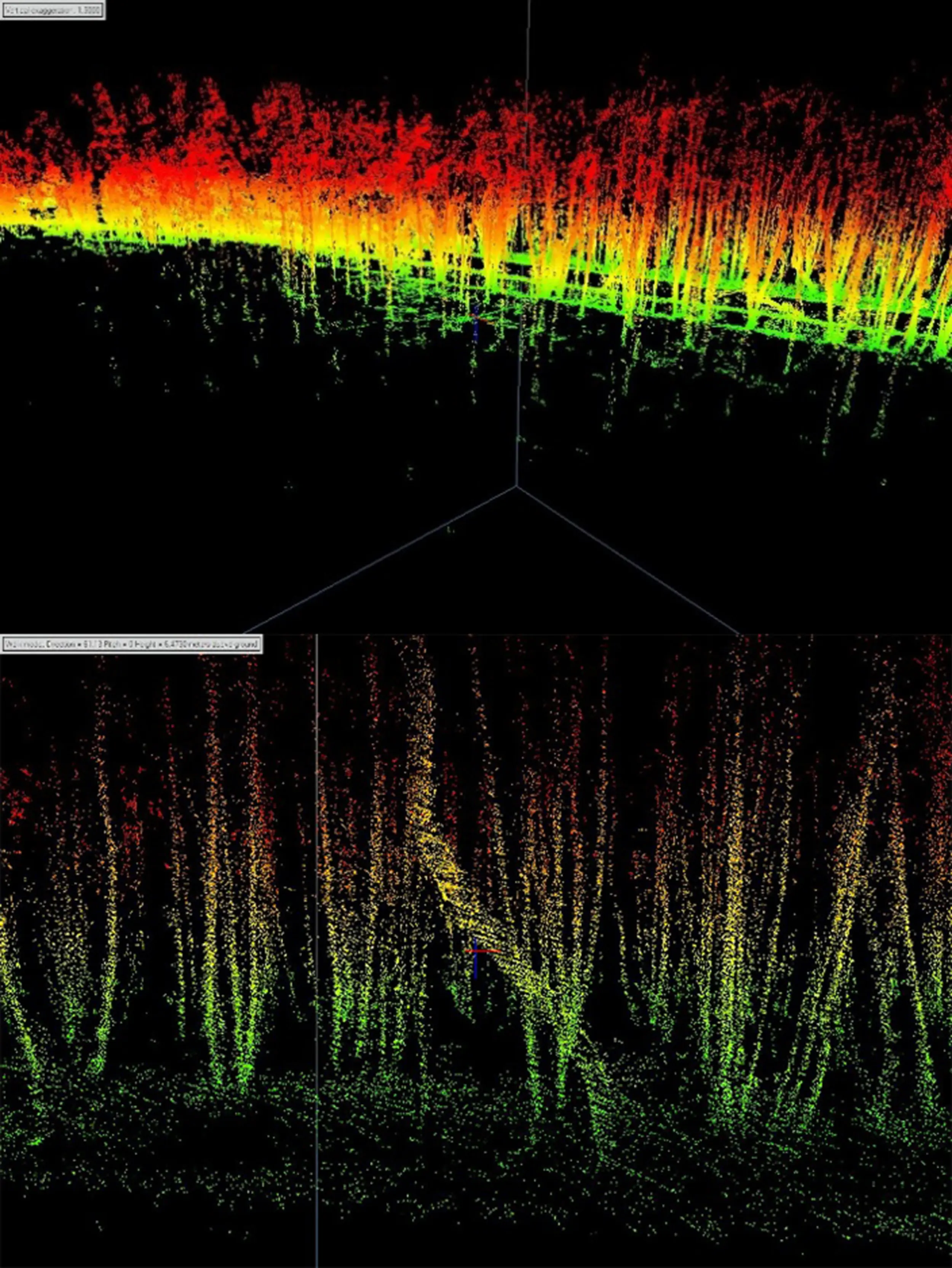
The ActiRS4Env project (Project ID: 23LCG-1E016), a state-funded initiative running from 2023 to 2028, includes a pilot research component aimed at assessing the feasibility of applying RADAR and LIDAR systems for the qualitative and quantitative evaluation of above-ground living biomass (AGB) in various natural and manmade ecosystems across Armenia.

Shushanik AsmaryanCorrespondence Contact to make official submissions to the GEO Secretariat on behalf of GEO Principal of Armenia Deputy Director for Science/Head of GIS and Remote Sensing Department Center for Ecological-Noosphere Studies NAS Armenia
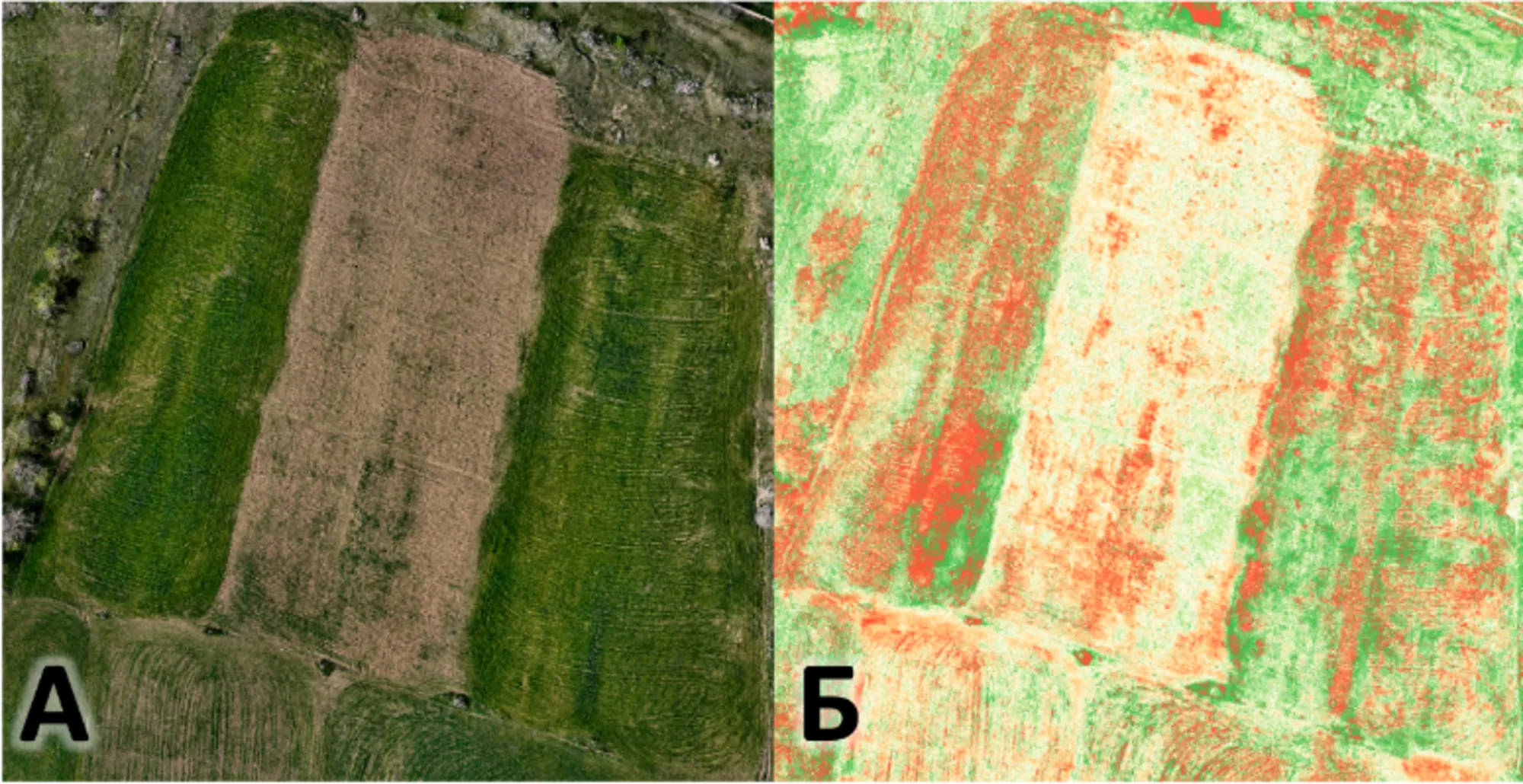
Project ID: 22IRF‐04 (2022–2027) is a state-funded initiative focused on developing methods for acquiring and analyzing the spectral signatures of natural and manmade objects in Armenia using ultra-high-resolution remote sensing data.

Shushanik AsmaryanCorrespondence Contact to make official submissions to the GEO Secretariat on behalf of GEO Principal of Armenia Deputy Director for Science/Head of GIS and Remote Sensing Department Center for Ecological-Noosphere Studies NAS Armenia
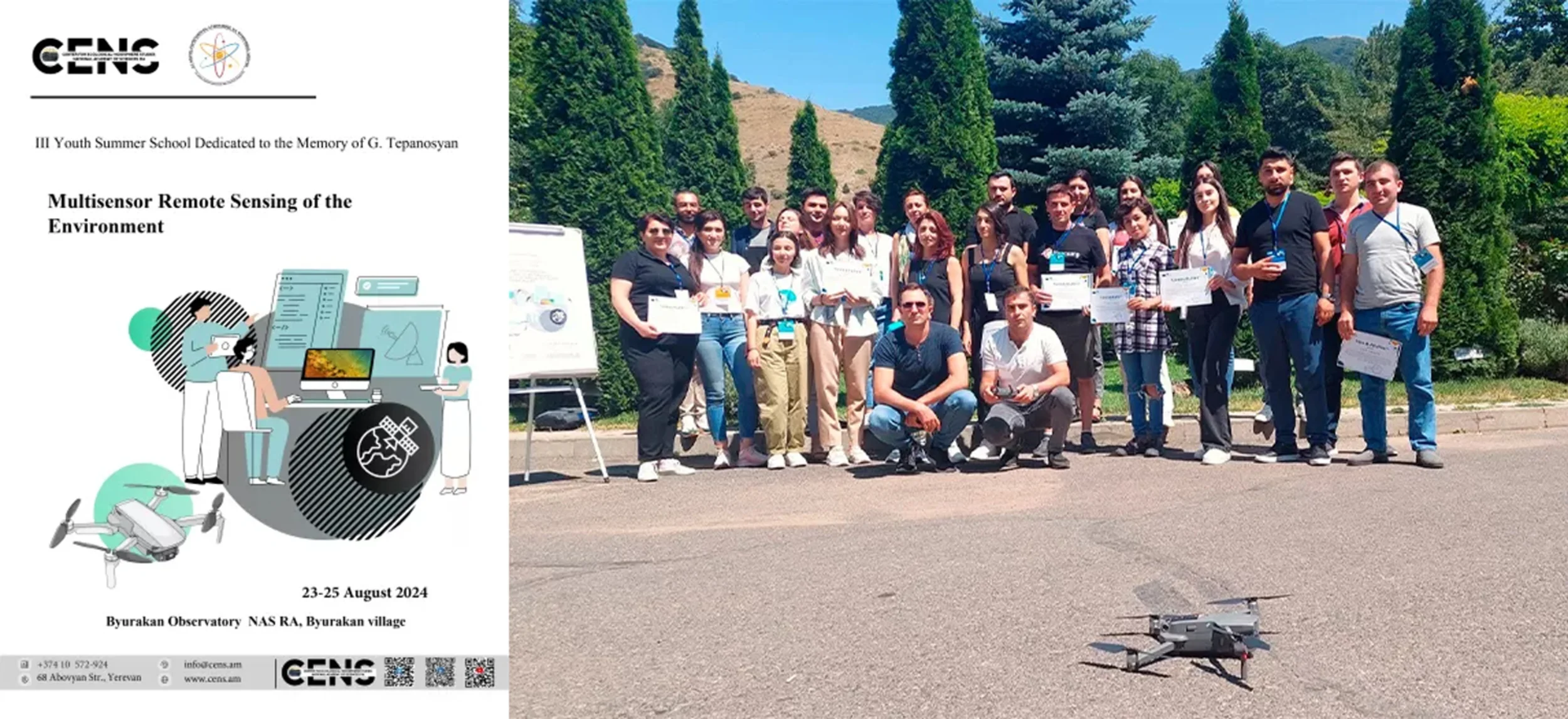
A series of seasonal schools (summer and autumn) is organized annually by CENS aimed to build and reinforce the research capacities of young and early carrier researchers in Earth Observation In Armenia.

Shushanik AsmaryanCorrespondence Contact to make official submissions to the GEO Secretariat on behalf of GEO Principal of Armenia Deputy Director for Science/Head of GIS and Remote Sensing Department Center for Ecological-Noosphere Studies NAS Armenia

The Center for Ecological-Noosphere Studies NAS Armenia has expressed strong interest and will in supporting leading GEO initiatives, such as the Global Ecosystem Atlas (https://globalecosystemsatlas.org/), which is planned to be presented at COP17, to be held in Armenia in 2026.

Shushanik AsmaryanCorrespondence Contact to make official submissions to the GEO Secretariat on behalf of GEO Principal of Armenia Deputy Director for Science/Head of GIS and Remote Sensing Department Center for Ecological-Noosphere Studies NAS Armenia


Australia

Canada
Canada continues to benefit from the exchange of knowledge and expertise through GEO, AmeriGEO, and our national GEO community. More than ever, international collaboration and continued access to open Earth observations is fundamental to addressing key global challenges, including climate change, biodiversity loss, and pollution. The Post-2025 Strategy is an important step and a clear demonstration of our commitment to innovation, knowledge-sharing, and international cooperation.

David HarperGEO Principal for Canada, and Director General, Satellite Earth Observations, Environment and Climate Change Canada
GEO BON, is a network of over 3,600 members across 152 countries worldwide, advancing research and collaboration to support a Global Biodiversity Observing System. GEO BON’s global conference "Living Data/Datos Vivos" in Bogota Oct 21-24, 2025, will convene its community to exchange knowledge and demonstrate progress in the development of biodiversity observation networks, monitoring practices and open data and platforms, such as BON in a Box. These advancements facilitate the global access of biodiversity data and the development of indicators for biodiversity conservation. In addition, GEO BON continues to provide monitoring science in support of the implementation of Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework of the UN Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD decision 15/5). This year GEO BON will participate in UN CBD regional and sub-regional dialogues offering guidance and training on the means to implement indicators within national monitoring frameworks.

Andrew GonzalezProfessor McGill University, Liber Ero Chair in Biodiversity Conservation, co-chair of GEO BON, and Quebec Centre for Biodiversity Science Director


Committee on Space Research
"At COSPAR, we strongly support GEO’s work to make satellite-based Earth science data widely accessible. But it’s not just about open access data, we also critically need proper documentation. Data documentation published in Peer-reviewed journals help solve this issue as they provide reliable, long-lasting explanations of datasets, including validation, accuracy and structure. Through our Capacity Building Workshops, we’re helping expand the expertise needed globally, and we see documentation as a crucial step toward making this data truly usable, especially for newcomers to Earth observation, in support of GEO’s Post-2025 Strategy Goal number 4."

Jérôme BenvenisteChair of COSPAR Scientific Commission A


European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts
“Celebrating together 20 years of GEO and 50 years of ECMWF, ECMWF supports GEO’s ambitions on Earth Intelligence as a key partner in cooperation and coordination activities stimulating user driven solutions through combining Earth observation and other data with state-of-the-art modelling, predictions and scenario analysis.”

Vermoote StijnHead User Outreach and Engagement, ECMWF


EuroGeographics
The EuroGeographics pan-European data services, harmonised datasets align perfectly with the Post-2025 GEO Work Programme as an Enabling Mechanism. As a Participating Organisation, EuroGeographics working jointly with GEO, will increase the use of our members’ data and strengthening cooperation between National Mapping, Cadastral and Land Registration Authorities and Earth Observation Community to unlock earth intelligence.

Sallie Payne SnellSecretary General and Executive Director, EuroGeographics

Germany
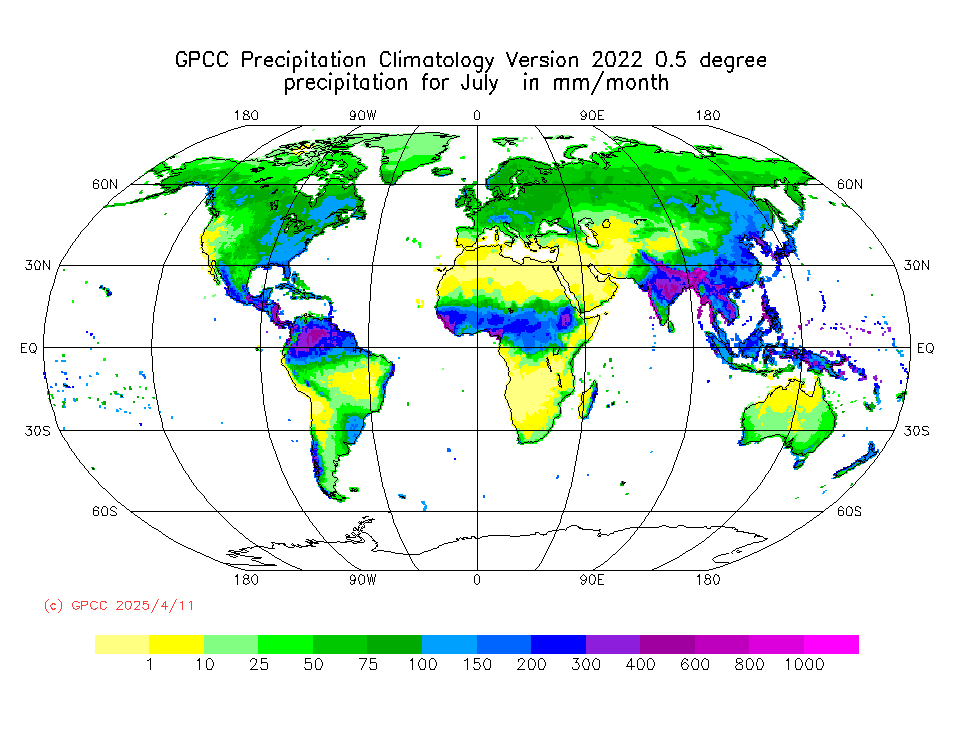
„The Global Precipitation Climatology Centre (GPCC), hosted by Germany’s meteorological service DWD under the auspices of the World Meteorological Organization (WMO), is by far the largest collection worldwide of quality-controlled station-based precipitation measurements. They are used to derive various gridded precipitation products for the Earth's land-surface, as e.g. maps of daily and monthly totals. These products are freely available to the international community and are regularly used in international assessments of the state of climate or water resources.“

Tobias FuchsMember of the DWD Executive Board, Director Climate and Environment Services
The hyperspectral German satellite mission EnMAP (Environmental Mapping and Analysis Program) measures key dynamic processes of Earth’s terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems by extracting geochemical, biochemical and biophysical parameters. Three years after launch, the scientific user community has demonstrated a variety of use cases based on EnMAP’s excellent data quality. User support is ensured through the online learning initiative HyperEDU, the EnMAP-Box toolbox and enhanced data accessibility alongside improved provision of Analysis-Ready Data.”

Godela RossnerHead of Department “Earth Observation”, German Space Agency at DLR
“End of 2024, the Federal German Ministry for Digital and Transport released the User Uptake Strategy of the Federal Government on satellite data for a connected and sustainable society. It is a crucial step towards making targeted and efficient use e.g. of the data and services of Earth observation programmes using satellites that have been continuously developed with great commitment for decades now. The German strategy is the result of a participatory process focusing on user needs. It provides a reliable framework to make optimum use of the opportunities and potential of satellite data and corresponding services for the common good.”

Dirk EngelbartDirector of Division Meteorology, Earth Observation and German Meteorological Service (DWD), German Federal Ministry for Digital and Transport


Ghana
“Through sustained collaboration with the GEO community, Ghana is deepening its commitment to leveraging Earth observation for national development. From launching our National Space Policy to applying EO tools in areas such as flood management, illegal mining, and green energy planning, we are steadily turning our GEO vision into action. By sharing our national GEO document with key stakeholders and scaling up pilot initiatives, we are laying the groundwork for a future driven by data, resilience, and sustainable growth.”
As part of Ghana’s contribution to the GEO community, the Ghana Space Science and Technology Institute (GSSTI) has undertaken satellite-based monitoring to estimate vegetation loss linked to environmental degradation and illegal mining. Between 2008 and 2024, Ghana recorded a total vegetation loss of approximately 59,841 hectares averaging 3,520 hectares per year. This Earth observation effort provides critical data to inform land use planning, guide restoration initiatives, and support sustainable policy enforcement. It also underscores Ghana’s commitment to leveraging EO data for environmental resilience and contributes valuable insights to the global GEO ecosystem.
The successful launch of the National Space Policy in 2024 marks a major milestone in establishing a unified national ecosystem for innovation, Earth observation, and international collaboration. This policy provides a strategic framework for integrating space-based technologies into national development, focusing on optimizing limited resources for maximum impact. It lays the groundwork for coordinated efforts in EO data utilization across sectors such as agriculture, disaster response, and climate resilience. The inclusive and forward-looking nature of the policy reflects Ghana’s commitment to building a data-driven, sustainable future aligned with GEO’s global vision.

Joseph Bremang TandohDirector, Ghana Space Science and Technology Institute (GSSTI)

Greece

Cambodia
Cambodia became the 104th member of the Group on Earth Observation (GEO) in 2017. The main vision for Cambodia GEO is to develop Data Cube in Cambodia and the future for monitoring natural resources and man-cause disasters such as flood, drought, rain storm, typhoon, thunderstorm, land slide, and deforestation as a part of SDGs implementation. To response this vision, Cambodia has been set up the project by using limited budget from the Royal Government of Cambodia. The main activities of this project are collecting data for primary data in the field and secondary data from relevant ministries and government institution involvement. The Cambodia GEO will also use the satellite data sharing from GEO member countries combine with social economic data has collected from survey and government institution involvement. Due to rapid population growth which causes the increase of urbanization, some land has transformed from rice field to settlement and other land uses giving negative impacts to environment such as water pollution and poor sanitation. The survey has shown that the infrastructure has broken by flooding and the household who living in along the river has also affected by flooding. The rise river water has decreased gradually, raining fall is irregularly and the air temperature in Cambodia during dry season is significantly high approximately 34OC to 35OC in the past few years. The survey shows that this year the temperature fluctuates very much in both dry and wet seasons which is too cold in wet season and too hot in dry season and is considered as the cause by the global warming.

Kimhor MengDeputy Director General, National Institute of Statistics, Ministry of Planning, Cambodia and as Cambodia GEO Principle
Due to rapid population growth which cause the increase of urbanization, some land has transformed from rice field to settlement and other land uses giving negative impacts to environment such as water pollution and poor sanitation. Cambodia GEO has started activities by collecting data for primary and secondary data relate to Disaster, Environment and Climate change. This result will be used for government to formulate policy for disaster, environment impact and climate change existing data. The main vision of Cambodia GEO is willing to develop « Data Cube in Cambodia ». The data cube will be combined with the primary and secondary data of social economic data collected with Earth Observation data.

Kimhor MengDeputy Director General, National Institute of Statistics, Ministry of Planning, Cambodia and as Cambodia GEO Principle

International Institute for Geo-Information Science and Earth Observation
ITC-is part of the Open Science network. ITC is actively involved in several GEO flagships and initiatives as participants in regional events, as members of the sub-groups or as co-chairs. Our mission is institutional strengthening in and with partners in the Majority World.

Freek Van Der MeerDean ITC

Being part of the global GEO network assures the sharing of knowledge and provides opportunities for collaboration and co-creation of tools, training/education materials and innovative technologies. We apply earth observation data and geoinformation science in four profiling themes which are closely aligned with GEO’s priorities: GEO AI, Resource Security, Urban Futures and Disaster Resilience.

Freek Van Der MeerDean ITC


Italy
Italy is strengthening the coordination amongst national experts involved in Earth Observation (EO) domains through the GEO-ITALY Group (www.geoitaly.org).
The GEO-ITALY overarching goal is to reinforce the synergies amongst involved institutions in Italy, thus facilitating a broad range of capacity building and outreaching activities to stakeholders and policy makers both at national and international level.
Members of GEO-ITALY are scientists, researchers and managers employed in several Institutes of the National Research Council of Italy, in the National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology (INGV), in the Italian National Institute for Environmental Protection and Research (ISPRA), in many other public institutions in the Country, such as the Italian Space Agency (ASI) and the Euro- Mediterranean Centre on Climate Change (CMCC), as well as in private companies such as PLANETEK, e-GEOS, MEEO, Latitudo 40 and TEAMDEV.
GEO-ITALY goal is to support the achievement of goals and objectives of the GEO post-2025 Strategic Implementation Plan and its work program for 2025-2030 period, through an active participation to the various GEO initiatives, flagships and incubator programs.

Nicola PirroneResearch Director of CNR & GEO Principal of Italy

The Global Observing System for Mercury (GOS4M) Flagship main challenge is to foster the sharing of monitoring data and modelling tools to support the policy implementation.
GOS4M (www.gos4m.org) is aimed to federate existing networks, monitoring programmes and observing infrastructures – currently it provides a link to the Global Mercury Observation System (GMOS – www.gmos.eu) and major existing regional networks. During the last year GOS4M developed the Knowledge Hub aimed to support the achievement of the objectives of international programmes and conventions related to mercury pollution which include UNEP, Minamata Convention on Mercury (MCM) Secretariat, UNECE-LRTAP and 2030 UN Agenda on SD. Special attention is paid to support all interested Parties in the implementation of the MCM. To this end global comparable monitoring data, validated models and policy interoperable tools are provided as part of the GOS4M Knowledge Hub designed to evaluate the relationship between cause and impact of mercury contamination, analyse cost-effective strategies aiming at reduce the mercury contamination at regional and global scale and co-design policy scenarios aiming to achieve the target of the MCM.
GOS4M is contributing to the GEO Knowledge Hub enabling open access to core data, tools, and applications, which are essential to delivering on the vision of “Earth Intelligence for All”. The GOS4M implements the GEO’s Open Data Sharing Principles and Open Knowledge framework for delivering actionable information to users, stakeholders and decision makers.

Sergio CinnirellaCNR - Institute of Atmospheric Pollution Research

Italy is continuing its longstanding activity to enhance the discovery and accessibility of data, information, and knowledge. It supports the GEO effort for an open and public infrastructure for data sharing and knowledge generation to deliver Earth Intelligence according to the GEO Statement for Open Knowledge. Italy carries out activities for facilitating data sharing developing the Discovery and Access Broker (DAB), and for knowledge generation and management developing the Virtual Earth Laboratory (VLab), a knowledge platform for model sharing and running in multicloud environments. Italy is co-chair of the GEOSS Platform Operation Team (GPOT) and member of the GEO Infrastructure Development Task Team (GIDTT). It also participates to the activity of the GEO Data Working Group and its sub-groups. For the advancement and evolution of the GEO infrastructure, collaborations are ongoing with ESA, EC-JRC, USA (USGS), Germany (DWD), Switzerland (University of Geneva), China (Ministry of Science and Technology).

Paolo MazzettiActing Director, CNR - Institute of Atmospheric Pollution Research
A private sector perspective:
MEEO, as a pioneer in remote sensing and environmental data services since 2004, focuses on transforming raw satellite data into actionable insights. MEEO’s expertise extends to AI-powered geospatial analytics, enabling the development of sophisticated products and services for environmental monitoring, land management, and disaster management. The ADAM platform, a key offering from MEEO, provides user-friendly access to a wealth of geospatial data, underscoring their commitment to democratizing access to environmental information derived from Earth observations. The long-standing partnership with the European Space Agency (ESA) further fuels the innovation in EO data exploitation, confirming the significant role within Multi-Mission Algorithm and Analysis Platform (MAAP), Destination Earth (DestinE) Platform, Global Development Assistance Analytics and Processing Platform (GDA APP), and many other initiatives.

Marco FoleganiMEEO

A further contribution of Italy to the many GEOSS Ecosystems tasks is offered by the GEO ECO (GEO Global Ecosystem) Community Activity and Action Group, co-lead by CNR. GEO ECO builds up and extends the approach used in the European Horizon 2020 ECOPOTENTIAL project, led by CNR, and from a few other initiatives, to other protected areas in Europe and in other continents.
GEO ECO aims to use available Earth Observation data, research results and tools on a global scale for enhancing knowledge on natural ecosystems, identifying protected areas (PAs) of international relevance as focus areas for its activities, as they are aimed to preserve natural ecosystems, and thus have a high intrinsic value for human societies. In Italy, a key PA will be the Gran Paradiso and the Alta Murgia National Parks, also involved in ECOPOTENTIAL, the former H2020 project on Earth Observation data for ecosystems in protected areas supporting GEO (2015-2019). The detection and modelling of the state and development of natural ecosystems in PAs is a priority for the monitoring the advancement of the SDG 14 and 15. It also extends its analysis to unprotected areas.
GEO ECO is adopting the view of ecosystems as "one physical system" with their environment, characterized by strong geosphere-biosphere-anthroposphere interactions across multiple space and time scales. The GEO ECO implementation plan can be downloaded here: www.earthobservations.org/documents/gwp20_22/GEO-ECO.pdf

Antonello ProvenzaleResearch Director CNR - Institute of Geoscience and Earth Resources

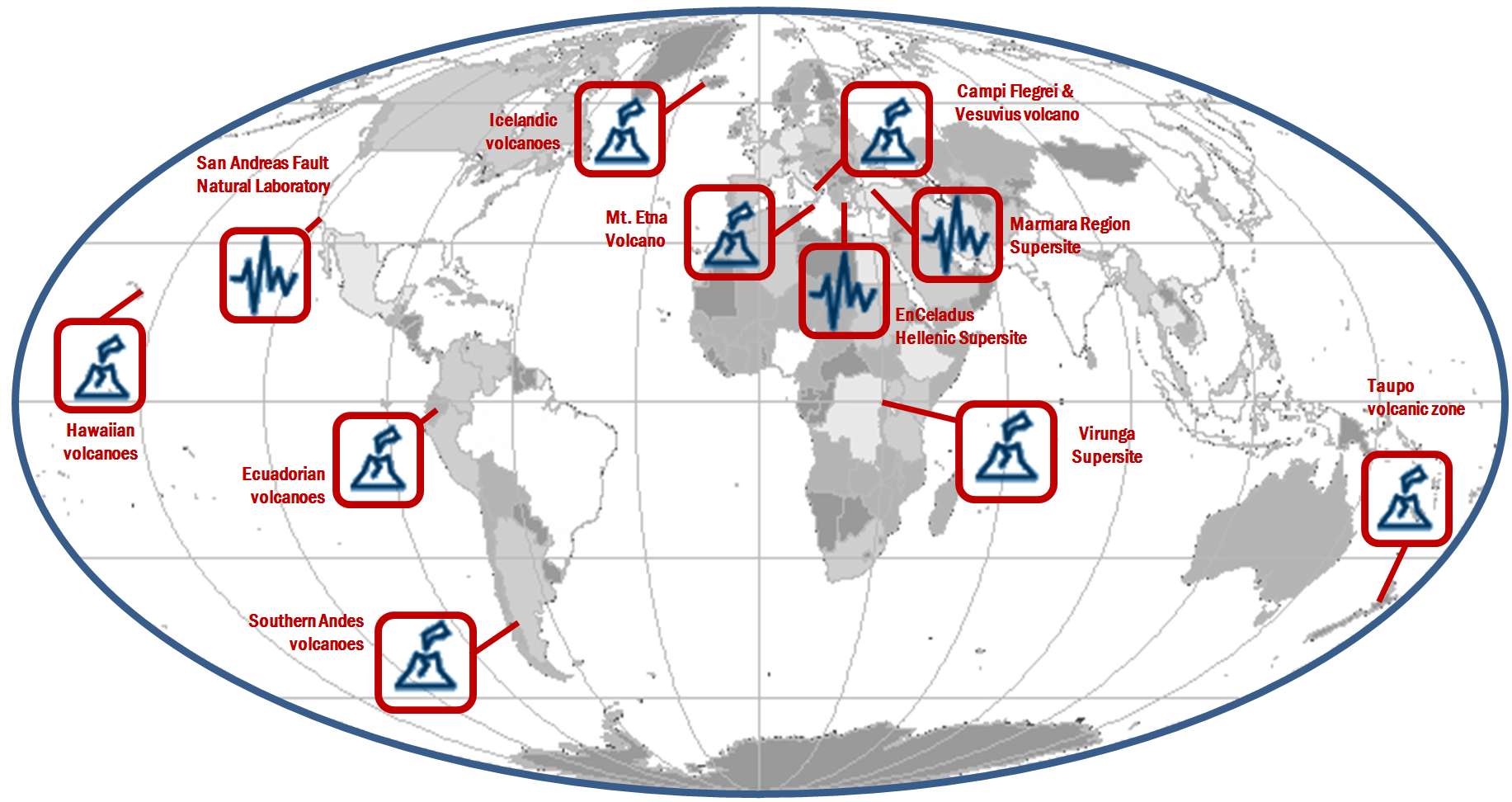
The Italian Space Agency (ASI) actively supports GEO Initiatives related to Disasters Risk Reduction (DRR) like GEO Geohazard Supersites and Natural Laboratory initiative (GSNL), a voluntary international partnership aiming to improve, through an Open Science approach, geophysical scientific research and geohazard assessment in support of DRR. ASI regularly provides thousands of products from its national asssets (mainly COSMO-SkyMed but also PRISMA and SAOCOM, in the latter case over ASI Zone of Exclusivity (ZoE)) to all the 13 Supersites and Natural laboratories all over the world, which represent multi-hazards pilot projects aiming at demonstrating the value of earth observation data for DRR as well as to build regional capacity in this sector.

Giovanni Rum & Antonio Montuori Agenzia Spaziale Italiana

Italy, through the INGV, coordinates and supports with important in-kind resource, the GEO-Geohazard Supersites and Natural Laboratories initiative (GEO-GSNL), established in 2010 under the Disaster SBA. GSNL is a network of 11 Supersites where a large community of scientists works to generate products for science-based decision making in Disaster Risk Management. GSNL is supported by the CEOS space agencies with satellite imagery and by a number of local monitoring agencies with in situ data. Supersite scientists openly share their in-situ and satellite data, promoting an Open Science approach and focusing on the sharing of scientific knowledge, capacity development, and technological innovation to increase the societal benefit geohazard science. All the Supersite coordinators are authoritative actors in the national frameworks for disaster prevention and response, and as such they constantly deliver hazard information generated for the Supersite, to the national decision makers, ensuring rapid and direct societal benefit of scientific findings.
The Italian Space Agency (ASI) also supports GEO-GSNL, providing, on a continuous basis, over 2500 COSMO-SkyMed products per year that are key for achieving the GSNL objectives.

Stefano SalviNational Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology - INGV
The Italian Space Agency (ASI) has launched on 22 March 2019 the PRISMA satellite carrying an hyperspectral sensor with a Ground Sampling Distance (GSD) of 30 m and covering the wavelength range from 400 nm to 2500 nm, with 10 nm spectral sampling. The launch was successful and the in-orbit commissioning has been completed, allowing PRISMA data to be accessible since May 2020 through the dedicated portal https://prisma.asi.it/. Data policy is based on a quasi-open and free access, with limitations on products per user quantities and on priorities for acquisition requests conflicts solving, to cope with the operational capabilities of the mission. Data policy allows commercial exploitation of value added product/services still delivering free of charge but forbids PRISMA original data redistribution. PRISMA catalog is now visible through GEOSS.

Giovanni Rum & Ettore Lopinto Italian Space Agency

Italy is supporting the GEO and UN-Habitat “Earth Observation Toolkit for Sustainable Cities and Human Settlements” Programme. The Programme participates in the EO4SDG Initiative and aims at developing a customizable and continually updated toolkit on the integration of Earth Observation and geospatial information into the urban monitoring and reporting processes on SDG targets and indicators based on inputs from UN Member States and cities. The CNR-IIA indicator estimation approach consists of deriving and updating, from Earth Observation data, some essential variables for the urban ecosystem: the spatial distribution and density of urban population and settlement maps. By integrating these essential variables with other domain-specific information i.e., the particle pollutant maps, specific urban resilience indicators and sub-indicators can be quantified. The case study focuses on updating the distribution map of the migrant population regularly residing in Bari and neighboring municipalities to monitor progress on the inclusiveness and sustainable urbanization targets of the SDG 11 of the UN 2030 Agenda.

Mariella AquilinoCNR - Institute of Atmospheric Pollution Research

Italy contributes to the GEO-LDN initiative for monitoring by RS data the conditions prone to Land Degradation and Desertification. CNR-IIA leaded the LIFE Preparatory Project NewLife4Drylands (www.newlife4drylands.eu) (2021-2024) and now coordinates the Earth Observation Work Package of the HE MONALISA (www.monalisa4land.eu) project (2024-2028), working on the computation of the SDG 15.3.1 indicator of the UN 2030 Agenda. Such estimate at local scale integrated with additional sub-indicators related to the local pressures and threats can support the decision-making process in the framework of preservation and restoration actions.

CRISTINA TARANTINOCNR - Institute of Atmospheric Pollution Research

The Italian National Copernicus User Forum is an instrument of the Presidency of the Council of Ministers aimed at fostering interaction among different user communities (Institutions, Research, and the Private Sector) for the sharing of information related to the Copernicus programme and the collection of user needs. The Forum's goal is to systematize the requirements expressed by users in order to maximize the development and use of Earth Observation products and to identify development priorities by defining a coordinated national position having a significant impact on the expansion of the Copernicus programme.
The National Forum is composed of representatives from various user communities, including public institutions and bodies, organizations dedicated to research and education, private and commercial entities, charities, non-governmental organizations, and international organizations that benefit from Copernicus data and information. The Forum take advantage also of thematic user consultation groups. Each representative coordinates and gathers the needs and contributions of their respective communities in order to influence the development of the European Programme. ISPRA (Italian Institute for Environmental Protection and Research) ensures the technical secretariat activities and provides technical support for coordination.
Coordinated by the national delegate to the Copernicus Committee and alternate to the European User Forum, the Italian Forum serves as the information and communication tool of the Presidency of the Council of Ministers on the European and national developments of the Programme. It is the venue where the needs of national users for the use of Copernicus products are coordinated, and where a harmonized and agreed position is ensured at the European level.

Andrea TaramelliDeputy Delegate to the Copernicus Committee

Italy is contributing to AfriGEOSS, by the EC Project PanAfGeo+ - Support to Geological Science and Technology.
PanAfGeo+ is the 3rd phase of a long-term PanAfGeo programme, a unique pan-African geosciences training project, based on cooperation between the African Union and the European Union.
Co-funded by the European Union and a consortium of European geological surveys since 2016, PanAfGeo is helping to strengthen collaboration between the associations of European geological surveys (EuroGeoSurveys) and African geological surveys (OAGS), as well as contributing to the Africa-EU partnership.
PanAfGeo+, with a 4-years duration (2025-2029), represents a follow-up of the previous two phases, the first between 2016 and 2019 and the second between 2021 and 2024. Overall, the PanAfGeo programme represents an investment of around €45 million.
The project supports the training of geoscientific staff from African Geological Surveys through the development of an innovative training programme aiming at increasing African-owned geological knowledge and skills for sustainable mineral exploitation and related infrastructures, and natural disaster prevention and mitigation. Specifically, the PanAfGeo programme enhances the capacity and role of African national Geological Surveys;
- Contributing to mineral resource assessments by national Geological Surveys in Africa;
- Increasing the activity of national Geological Surveys in regional mapping and exploration to upgrade their geoscientific information base and mineral inventories;
- Strengthening the level of geological knowledge and skills in national Geological Surveys through training;
- Strengthening OAGS’ potential to meet the needs of the African continent.
Capacity building has been so far addressed to over 1,750 geoscientists from the 54 African countries with the organization of 72 short- and medium-term trainings in 22 African host countries. The training sessions focused on a wide range of geosciences topics such as satellite imagery analysis, geological mapping through GIS techniques, geo-hazards geochemistry and analytical chemistry, economic geology, mineral exploration.
ISPRA is currently involved in PanAfGeo+ in the following WPs: Geoscientific Mapping, Mineral Resources Assessment, New Frontiers in Geosciences, Geohazards and Environmental Management of Mines.
More details of the project in: https:// panafgeo.eurogeosurveys.org

Giuseppe DelmonacoGeological Survey of Italy, Italian Institute for Environmental Protection and Research (ISPRA)

Italy is part of the EuroGEOSec project consortium, which is aimed to support the EuroGEO vision and to prepare the transition of the EuroGEO initiative into a sustainable endeavor, by setting-up a EuroGEO secretariat.
The overarching goal of the EuroGEOSec project is to support the coordination of the EuroGEO initiative and develop a sustainability plan guiding its long-term operation. This will be achieved by establishing the EuroGEO Secretariat with the mission to (i) strengthen GEO-related coordination mechanisms at European and national levels, (ii) support increased innovation, space application development and reinforcement of the European space data ecosystem concept; (iii) foster international cooperation to help stimulate the market and promote European technology and services; (iv) contribute to the European Green Deal objectives and the European strategy for data (EU Data Spaces) by further deploying and exploiting the use of EO towards a strengthened Global Earth Observation System of Systems (GEOSS).

Nicola PirroneResearch Director of CNR & GEO Principal of Italy

Italy is participating to the construction of the EIRENE RI (Research Infrastructure for EnvIRonmental Exposure assessmeNt in Europe), an ESFRI (European Strategy Forum on Research Infrastructures) infrastructure that is part of the national ESFRI roadmap since 2021, considered among the high-priority national RIs (PNIR 2021-2027 report). EIRENE aims to establish a sustainable research infrastructure enabling the advancement of exposome research in Europe by integrating the complementary capacities of European Member States, harmonizing and upgrading them to effectively address current scientific and societal challenges in the areas of chemical exposures and population health. EIRENE RI includes 21 national hubs and more than 50 individual partners. The contribution of Italy to EIRENE RI is through the National Node EIRENE RI – ITALY which is a Joint Research Unit (JRU) between the National Research Council of Italy (CNR), the Italian Space Agency (ASI), and the Italian National Institute of Health (ISS). The EIRENE-ITALY node integrates members’ competencies in various domains of Earth Observation data and technologies, Global Observing Systems, Forecasting Air Quality DSS (KHs, DTs), Near-surface Air Quality Validation, Bio-monitoring data, Epidemiology & Toxicology research, Exposome studies and Risk assessment. The preparatory phase of EIRENE RI (2022-2025) was addressed to establish advanced integrated services to enhance exposome research studies. In this framework, the Members of EIRENE-ITALY national node provide physical and/or virtual access to infrastructures (i.e., laboratories, observatories, and environmental networks) as well as to harmonized data and tools (knowledge Hub Platforms) according to FAIR principles. The overarching goal of EIRENE- ITALY is to foster a change of paradigm in linking environmental research with human exposure studies through a ONE HEALTH approach, where all major anthropogenic-related drivers are accounted for, that may lead to elaborate cost-effective strategies able to mitigate the risk associated to human exposure to major persistent contaminants.
The initiative will foster the GEO Health CoP and is part of GEO Flagship GOS4M and GEO Initiative GOS4POPs.

Francesca SprovieriResearch Director of CNR - Institute of Atmospheric Pollution Research

A private sector perspective: Downstream services by e-GEOS
e-GEOS, an ASI (20%) / Telespazio (80%) company, is a Global Leader in providing high technologic and innovative geoinformation services and platforms based on Artificial Intelligence and cloud technology with digital, fast and customized access covering all fields of the Geo-Spatial Information business. CLEOS, e-GEOS latest launch, is the Information cloud platform to unlock geoinformation value in AI-powered applications accessible through an enhanced user experience offering a direct market place access to customized products. e-GEOS offers a unique portfolio of application services, from data acquisition to the generation of analytics reports, also thanks to its radar capabilities and to the fast access to the superior monitoring capabilities of the COSMO-SkyMed constellation of first and second generation. e-GEOS has acquired also a leading position within the European Copernicus Program. e-GEOS application platforms include experienced and solid services for environmental protection, rush mapping in support to natural disaster management, specialized products for defense and intelligence, oil spill and ship detection, maritime surveillance and security, assets and critical infrastructures monitoring, landslides and ground subsidence analysis, thematic mapping for agriculture and forestry, climate change phenomena monitoring.

Fabio VolpeSenior Scientist, e-GEOS

A private sector perspective:
Planetek Italia is an Italian Benefit Company established in 1994, which employs 100+ women and men, passionate and skilled in Geoinformatics, Space solutions, and Earth science. Planetek provides solutions to exploit the value of geospatial data through all phases of data life cycle from acquisition, storage, management up to analysis and sharing. The company operates in many application areas ranging from environmental and land monitoring to open-government and smart cities, and including defence and security, as well as Space exploration and EO satellite missions.
Among its main activity areas, the development of software for the satellite on-board data and image processing leads to the creation of a new business model called SpaceEdgeTM. SpaceEdgeTM is a new concept of satellite as-a-service powered by an Artificial Intelligence (AI) enhanced processing framework embarked on satellites, which makes available in-orbit payloads, resources, and services on-demand: services include EO data acquisition, processing, actionable information extraction, downlink, and distribution. Information detected in Space is then transferred back to the Ground as notifications and alerts or directly exploited on-board in autonomous decision workflows. Useless data and information non-relevant to the application’s workflow can be discarded, saving memory, bandwidth and thus increasing the efficiency and quality of automated pipelines too.
The fields of application of on-board processing to reduce information latency are numerous, and will address GEO's priority engagement areas including the United Nations 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, the Paris Agreement, and the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction.

Giovanni Sylos LabiniCEO, Planetek Italia s.r.l.

A private sector perspective:
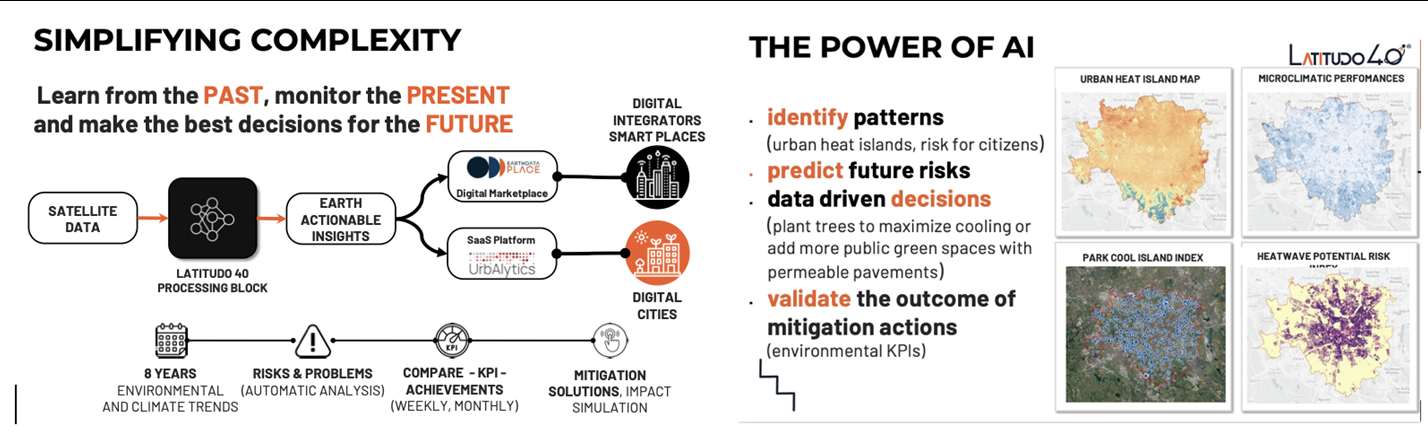
Latitudo 40 is a startup founded by four deep tech and space experts in 2017, which now employs a team of more than 15 people, with a predominance of Data Science experts for the development of new algorithms based on AI/ML and generative AI applied to the analysis and understanding of multi-spectral and hyperspectral satellite imagery. Latitudo 40, to make the most of the value of geospatial data, has invested in the development of a cloud-based platform to be used in SaaS mode for the analysis and monitoring of urban environments, with particular reference to the issue of planning sustainable and resilient cities of the future, identifying the main risks for the population and infrastructures (urban heat islands, urban heat risks, floods) and creating a map of intervention priorities for public decision-makers and urban planners, indicating possible mitigation actions using Nature Base Solutions. In addition, Latitudo 40 has developed a dataspace from space to foster the adoption of Geospatial solutions. In this space, system integrators and developers can find always-available datasets to understand urban risks better and create new applications in city monitoring, precision agriculture and infrastructure monitoring.
EarthDataPlace makes spatial datasets available to everyone easily, quickly and inexpensively.
Latitudo 40 supports the market with a vision of "learning from the past, monitoring the present and designing the sustainable place of the future", and to pursue this strategy, it has launched its Place Simulator. This environmental scenario simulator takes as "input" the different options for modifying the environmental scenario (changes in land cover/land use, new trees or green areas, etc.). It generates as "output" synthetic satellite images obtained with Generative AI to assess the impact of the different scenarios and identify the best solution for the environment.
The application areas of Latitudo 40 solutions provide a better and more detailed understanding of the variables that affect our environment and predominantly impact GEO's priority areas of endeavour, including the UN 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, the Paris Agreement and the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction.

Gaetano VolpeCEO, Latitudo 40
A private sector perspective:
TeamDev S.r.l. is an Innovative SME established in Perugia, Italy in 2008 specializing in information and communication technologies (ICT) with a strong focus on technological innovation, user interaction, and systems integration with third-party products. TeamDev has developed innovative solutions over the years at the national and international level in different application domains, from Artificial Intelligence (AI) to Earth Observation (OT) to Big Data, using a mix of technological skills such as: Development, Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and data modeling and analysis. With these characteristics the company has acquired a wide portfolio of clients, including: large companies (GOPA, ...), public administration (Umbria Region, Independence Oregon, ...), NGOs (Legambiente, Save The Children, ...) and international institutions (NATO, WMO, ...). The areas of relevance are numerous: Smart City (https://wise.town/en/), agriculture, development of complex systems for public administration and private companies, development of human-machine interfaces in the industrial field, and others. TeamDev is a Silver Partner of Esri (https://www.esri.com/partners/teamdev-srl-a2T70000000TWcWEAW) and Gold Partner of Microsoft and with advanced experience in using Microsoft Azure services. In addition, it is a FIWARE Gold Partner (https://www.fiware.org/), a founding member of the European Space coop. (https://spacecoop.eu/), a BDVA-DARIO partner (https://www.bdva.eu/), and participates in the faculty board and co-funds the 39th & 40th cycle National Doctoral Fellowships on Earth Observation (DNOT – Università degli studi di Roma “La Sapienza” coordinator).
WiseTown is our Smart City Platform able to develop a monitoring and predictive What if - Decision Support System for urban planning that improves citizens' quality of life, and increases the resilience and sustainability of cities. WiseTown provides an EO-based technological suite to monitor, predict, and optimize the effects of planned urban interventions.

Luciano ConcezziR&D Director TeamDEV srl
Japan
“ALOS-4 satellite has successfully been launched. With wider swaths than ALOS-2 without decreasing the resolution, ALOS-4 will unlock the new world by leveraging the merits of L-band SAR for disaster, forest, sea ice, agriculture and infrastructure monitoring.”

Hironori MaejimaSenior Chief Officer of Earth Observation Missions, Space Technology Directorate I, JAXA
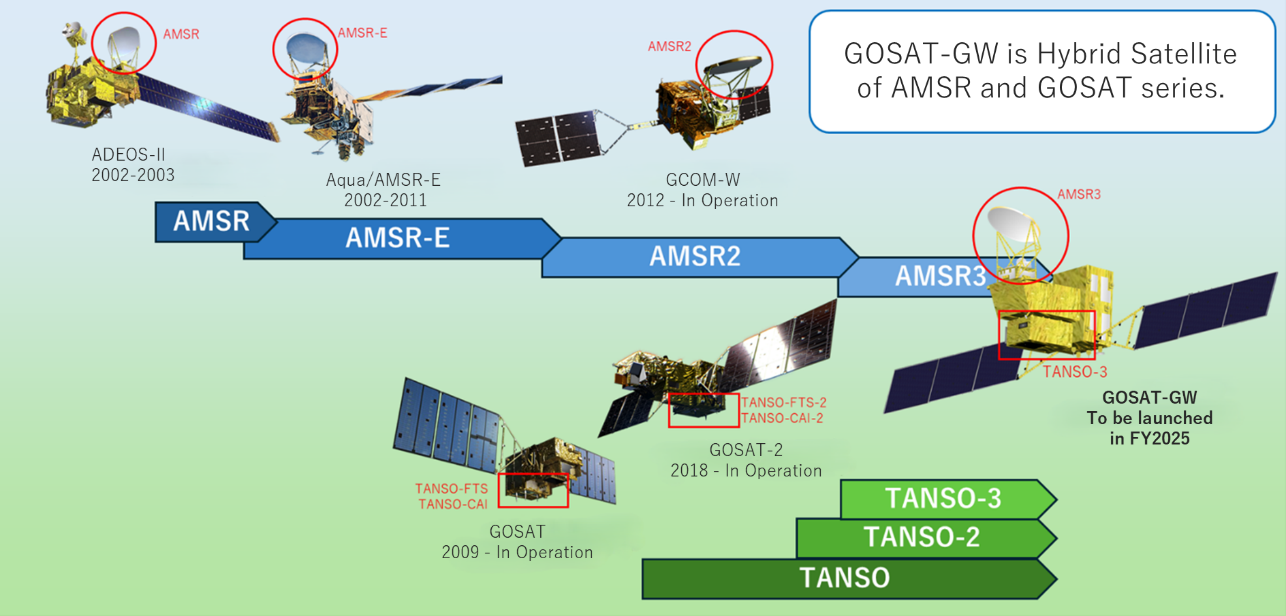
“GOSAT-GW, the third satellite of the GOSAT series with the third generation of Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer (AMSR) series, is scheduled to be launched in FY2025. More than 20 years of monitoring and beyond provide a basemap information for Earth Intelligence.”

Hironori MaejimaSenior Chief Officer of Earth Observation Missions, Space Technology Directorate I, JAXA
JICA aims not only establish the monitoring system but also enhance the skills of local enforcement officers and other personnel combating illegal deforestation by providing timely and accurate information, the project seeks to empower them to take effective action.

JICA

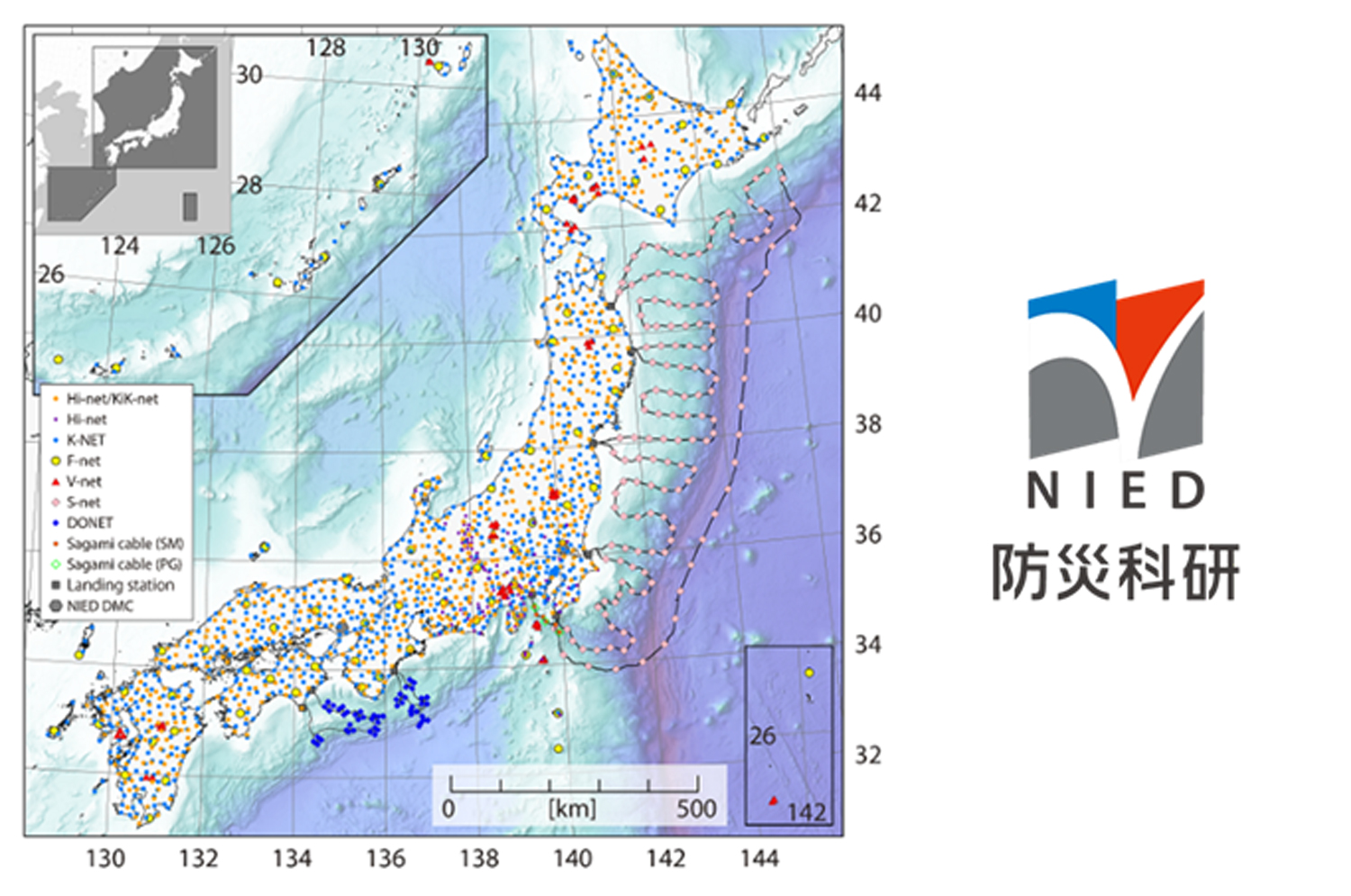
National Research Institute for Earth Science and Disaster Resilience (NIED) operates an integrated observation network, Monitoring of Waves on Land and Seafloor (MOWLAS), which consists of approximately 2,200 stations that provide comprehensive, accurate, and rapid observation and monitoring of earthquakes, tsunamis, and volcanic activity throughout Japan and its offshore areas. The application of real-time observations and the processing of MOWLAS data have contributed to disaster mitigation through measures such as earthquake early warnings and tsunami forecasts.

NIED National Research Institute for Earth Science and Disaster Resilience

Gambia, Republic of the
“Encouraged by GEO and the GEO Member Community we adopted an open EO data and knowledge policy in 2024. The use of EO data and its related services and products has since increased spectacularly. One measurable impact is an improved use of alternative energy sources and a reduction of our carbon footprint.”

Poncelet IlelejiJokkolabs Banjul, The Gambia


Red de Laboratorios de Observación de la Tierra para la Inteligencia Territorial de las Américas
“Collaboration and data sharing through Red LabOT have strengthened informed decision-making and accelerated regional responses to disasters and climate change, bringing Earth intelligence closer to those who need it most.”

Joana Doe Director, IGHTRDS


Nigeria
“Our collaboration with GEO has reinforced Nigeria’s leadership in Africa’s Earth observation landscape, enhancing regional synergy and promoting the GEO vision across institutions. GEO’s open data philosophy has enabled us to develop localized EO solutions and improve national early warning systems with real-time analytics across various sectors.”

James GodstimeDirector of Strategic Space Applications, National Space Research and Development Agency, (GEO-Nigeria Alternate Principal)
”Being part of GEO has greatly accelerated gender-inclusive innovations in Earth Observation (EO) applications for agriculture and climate action in Nigeria’s most underserved regions. Through GEO's support, we have been able to break longstanding barriers, empowering more women and youth in rural Nigerian communities to harness EO tools for sustainable agriculture and resource management. A Rural Community Woman's closeness to nature, her profound understanding, and essential connection breathe life into the natural world. Her unique bond and experiences in nurturing this relationship make her pivotal in preserving our environment. It's time to empower women to participate in climate change action.”

Jagila JantikuChief Scientific Officer, National Space Research and Development Agency. (Focal Point, GEO-Nigeria Desk Officer)

“Participation in GEO has strengthened Nigeria’s national EO policy framework. We are now aligning with open data principles and integrating EO insights into urban planning, disaster response, and environmental policy.”

Abayomi AlagaDirector of Mission Planning and Satellite Data Management, National Space Research and Development Agency. (Member; GEO Nigeria)

"Through the integration of Earth Observation data and the GEO-LDN Toolbox, we empowered local stakeholders in Amba, Nigeria, to restore 2 hectares of degraded land, strengthen sustainable land management practices, and build resilience against environmental challenges."

Shomboro KarauChief Scientific Officer National Space Research and Development Agency (GEO-Nigeria Member)

"Through the power of Earth observation and GEO, we have gained unprecedented insights into the impact of deforestation in Northern Nigeria revealing patterns, guiding action, and inspiring sustainable solutions for the future."

Princess Ifeyinwa Ezeanya Senior Scientific Officer National Space Research and Development Agency (Member; GEO- Nigeria)
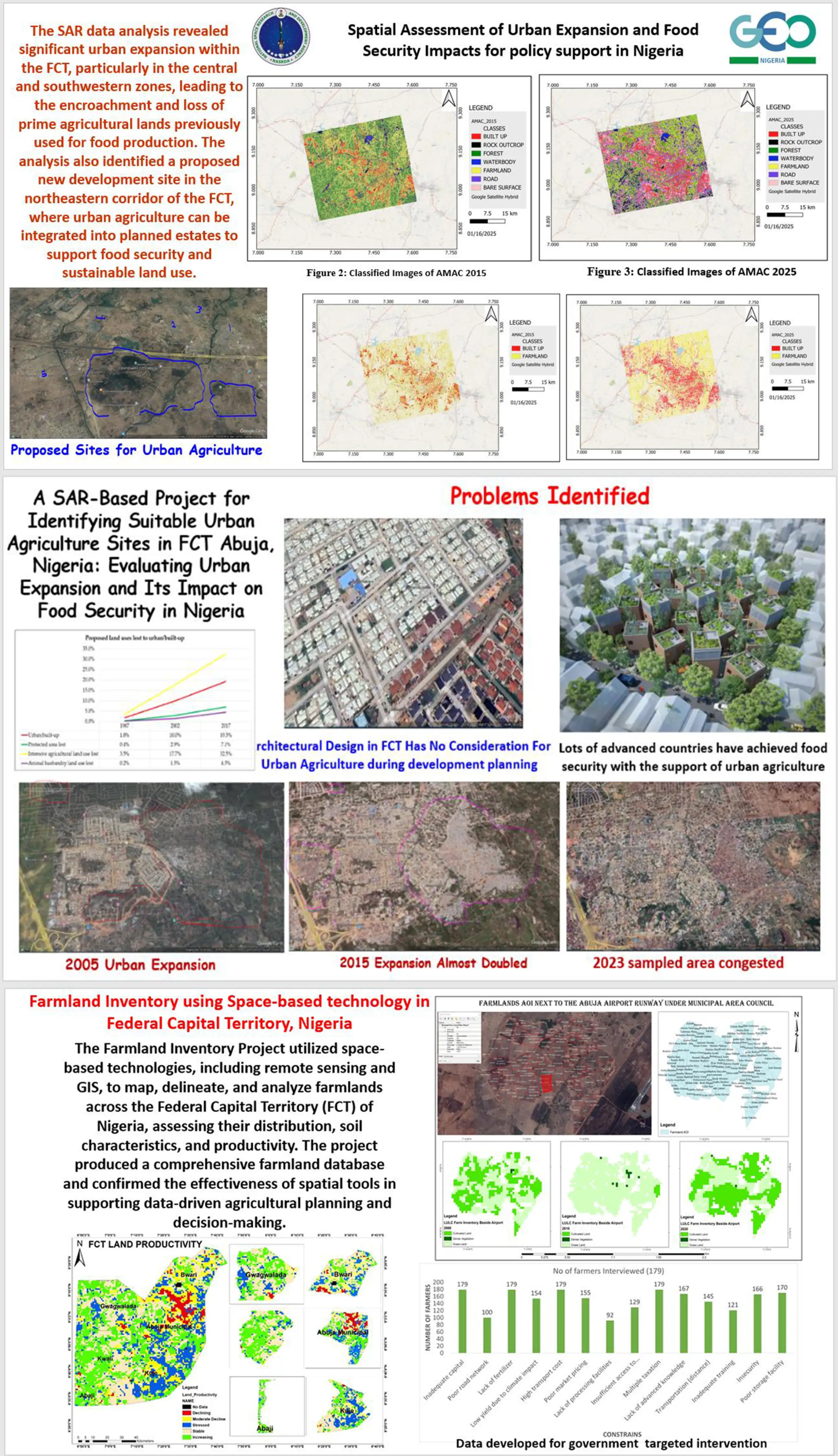
“Through GEO, Nigeria has significantly advanced its Earth observation capabilities, empowering policy with actionable data for climate resilience, food security, and sustainable urban development. With projects such as the Farmland Inventory and SAR-based analysis of urban expansion in the FCT, Nigeria is now generating geospatial intelligence that informs land use planning, protects agricultural resources, and strengthens food systems nationwide”.

Matthew AdepojuDirector General/Chief Executive, National Space Research and Development Agency (GEO-Nigeria Principal)

China
ChinaGEOSS Data Sharing Network has successfully established a national-level GEOSS infrastructures to integrate large number of archived satellite data, AI-ready data, scientific paper data and in-situ data. Facing the GEO engagement priorities, it provides more then 5300 datasets to international users through a unified data portal, ensuring easy and seamless access to a wide range of China’s Earth observation resources. It is also the main channel for domestic and international data exchanges, ChinaGEOSS completely shared 5.68 million data to GEOSS Portal from 2016 to 2024 and made a significant contribution to the implementation of AOGEO IPS project.

Lianchong ZhangDeputy Director of ChinaGEOSS Data Sharing Network, Aerospace Information Research Institute, the Chinese Academy of Sciences (AIRCAS)
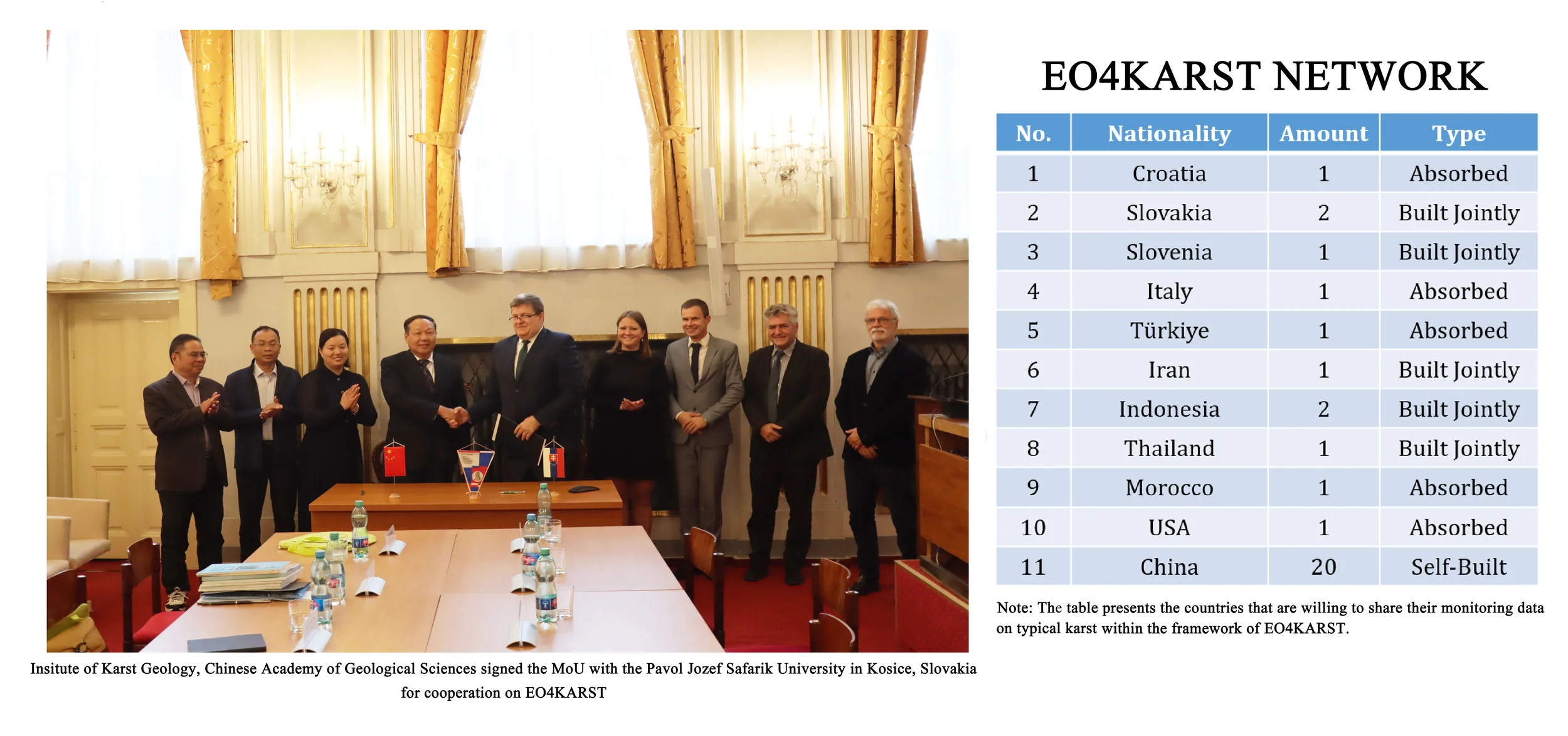
The Institute of Karst Geology (IKG) of Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, has conducted a pilot initiative during 2023 to 2025: Earth Observations for Global Typical Karst (EO4KARST) focusing on water resources, land use and related resources protection in typical karst areas globally. So far, EO4KARST has built up an observation network with 32 sites built or absorbed in this network by sharing the authorized data. An initial online platform for sharing and managing the data with the related APP is developed into trial operation stage, which is planned to be formally operated by the end of 2025. EO4KARST is hoping to provide a practical big data platform for assisting the sustainable development of the fragile karst areas all over the world.

Qukan LuoAssociate Professor of Institute of Karst Geology, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences
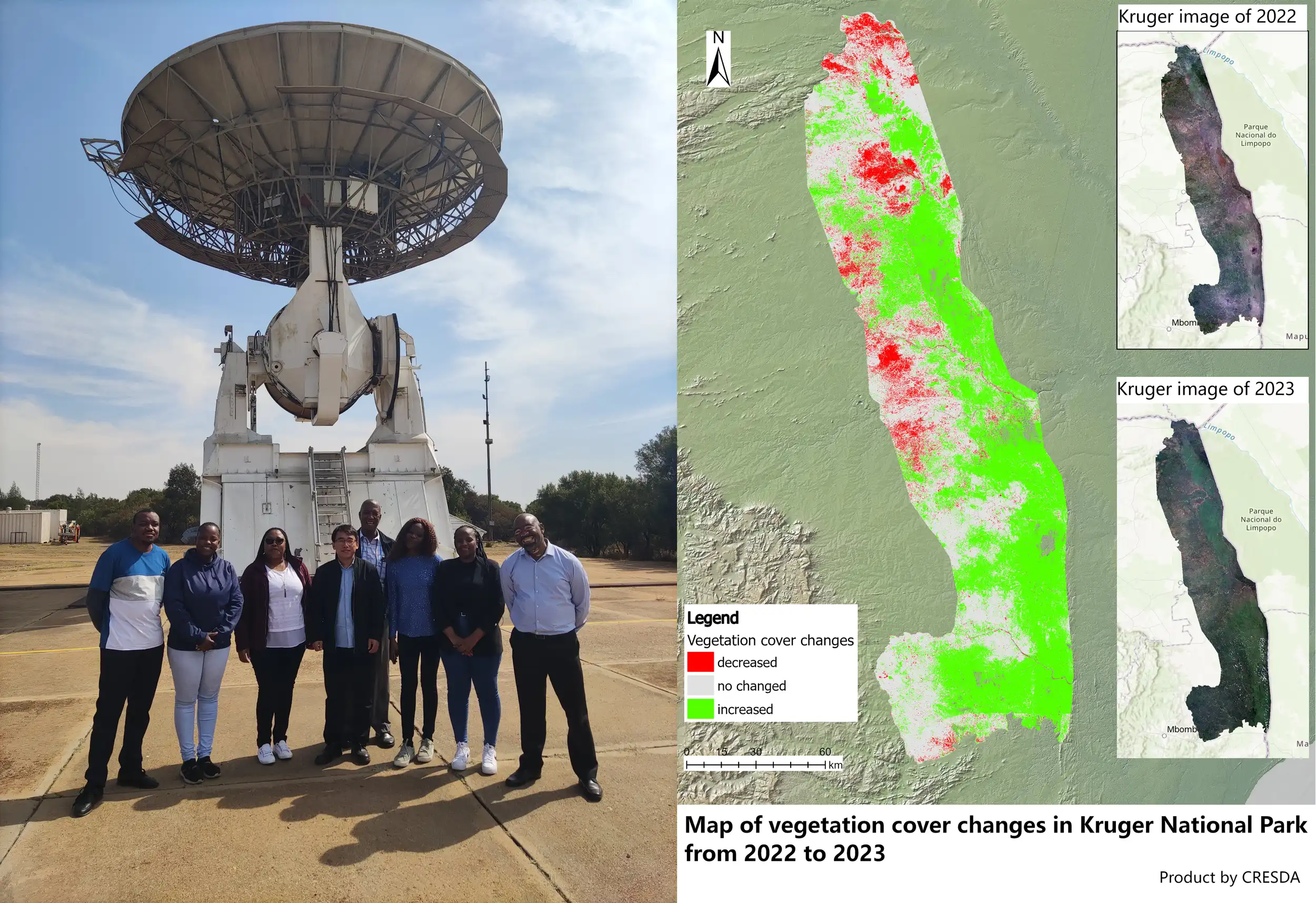
The China Brazil Earth Resources Satellite (CBERS) Data Distribution and Service Capacity Building Project for Southern Africa began at the fourth Plenary of GEO. In the past years, China Centre for Resources Satellite Data and Application (CRESDA) and South African National Space Agency (SANSA) have been working closely to realize the direct reception and processing of data from three satellites, CBERS-02B, CBERS-04 and CBERS-04A, at Hartbeeshock ground station in South Africa and the distribution in Southern Africa countries. These satellite data have played actively roles in disaster monitoring, environmental protection, land use and other fields. The project is one of the most successful practices of GEO to promote global data sharing, achieving common scientific and technological progress and promoting Earth observation technology to benefit mankind, and is also a successful case of space science and technology cooperation between China and South Africa.

Tao YueDirector General of China Centre for Resources Satellite Data and Application (CRESDA)
GEO China initiated the Collaborative Network of Disaster Data Response (CDDR) in 2016 in response to the GEO’s call for global coordinated disaster risk reduction. The CDDR mechanism has a membership of 34 China’s satellite agencies and 9 international Organizations, which contributes to the implementation of the UN 2030 Sustainable Development Goals. As of 2024, it had integrated 30 high resolution optical, radar, and hyperspectral satellites to cope with 56 major disaster emergency events such as earthquakes, floods, landslides, tsunamis and volcanic eruptions in 37 countries.

Xiang GaoDirector General of GEO China Secretariat, China Science and Technology Exchange Center
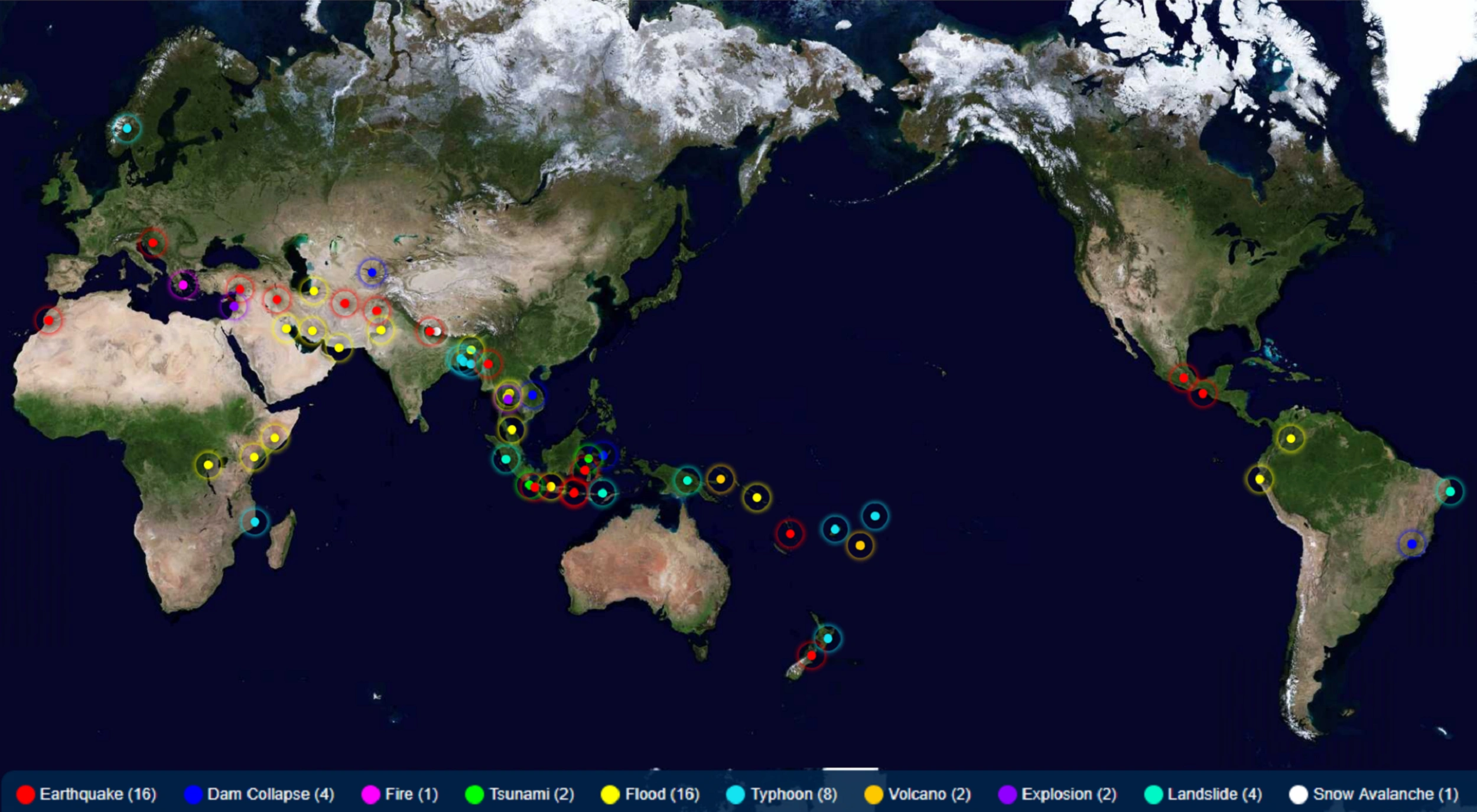
Chinese government in collaboration with relevant EO related authorities of African countries and ASEAN countries jointly build the China-Africa Cooperation Center on Satellite Remote Sensing Application (CACSA) and ASEAN-China Satellite Remote Sensing Application Centre (ACSAC), which uphold data-sharing network, carry out public goods development, satellite remote sensing monitoring and application demonstration, personnel training and exchange, so as to build a hub of knowledge sharing, experience exchange, and innovation in EO field. Moreover, Land Satellite Remote Sensing Application Center, MNR (LASAC) has jointly established 35 oversea nodes with 32 countries and 3 international organizations of Natural Resources Satellite Remote Sensing Cloud Service Platform (SatClouds) worldwide, shared more than 283,479 scenes within 9,857 baths and 369 TB of 2-meter resolution satellite images covering 112 countries and territories. These data have achieved the expected results in various domains of EO in the partner GEO Members.

GAO Xiaoming Deputy Director General, Land Satellite Remote Sensing Application Center, Ministry of Natural Resources of P.R.China

The Pengcheng Laboratory and the University of Hong Kong have introduced an innovative Global 30-m Seamless Data Cube (SDC 30), integrating multi-source satellite data. This advanced system systematically converts fragmented and noise-affected satellite observations into standardized temporal sequences, a better analysis-ready dataset. They are also sharing the first global near-daily wetland dynamics dataset produced from SDC30. The data are accessible through iEarth, a service system developed on the Pengcheng Cloud Brain II computing infrastructure. Over 6600 users from 75 countries and regions have registered and downloaded data from the iEarth platform (https://data-starcloud.pcl.ac.cn/iearthdata/).

Jie WangAssociate Research Fellow of Pengcheng Laboratory

Currently, China has eight Fengyun satellites in orbit, providing real-time data and products to users around the world. We have established a Fengyun satellite emergency support mechanism (FY_ESM) and developed a series of web-based satellite application service platforms (FY Earth and regional versions) to ensure rapid response and comprehensive use of Fengyun satellite data for global weather, climate and disaster monitoring. In the next two years, China will launch three Fengyun geostationary meteorological satellites to strengthen the global early warning system, support the United Nations "Early Warnings for All" initiative and the four major priorities of GEO, and provide support for decision-making and action.

WANG Jingsong Director General of National Satellite Meteorological Center (National Center for Space Weather) (NSMC/NCSW), China Meteorological Administration (CMA)
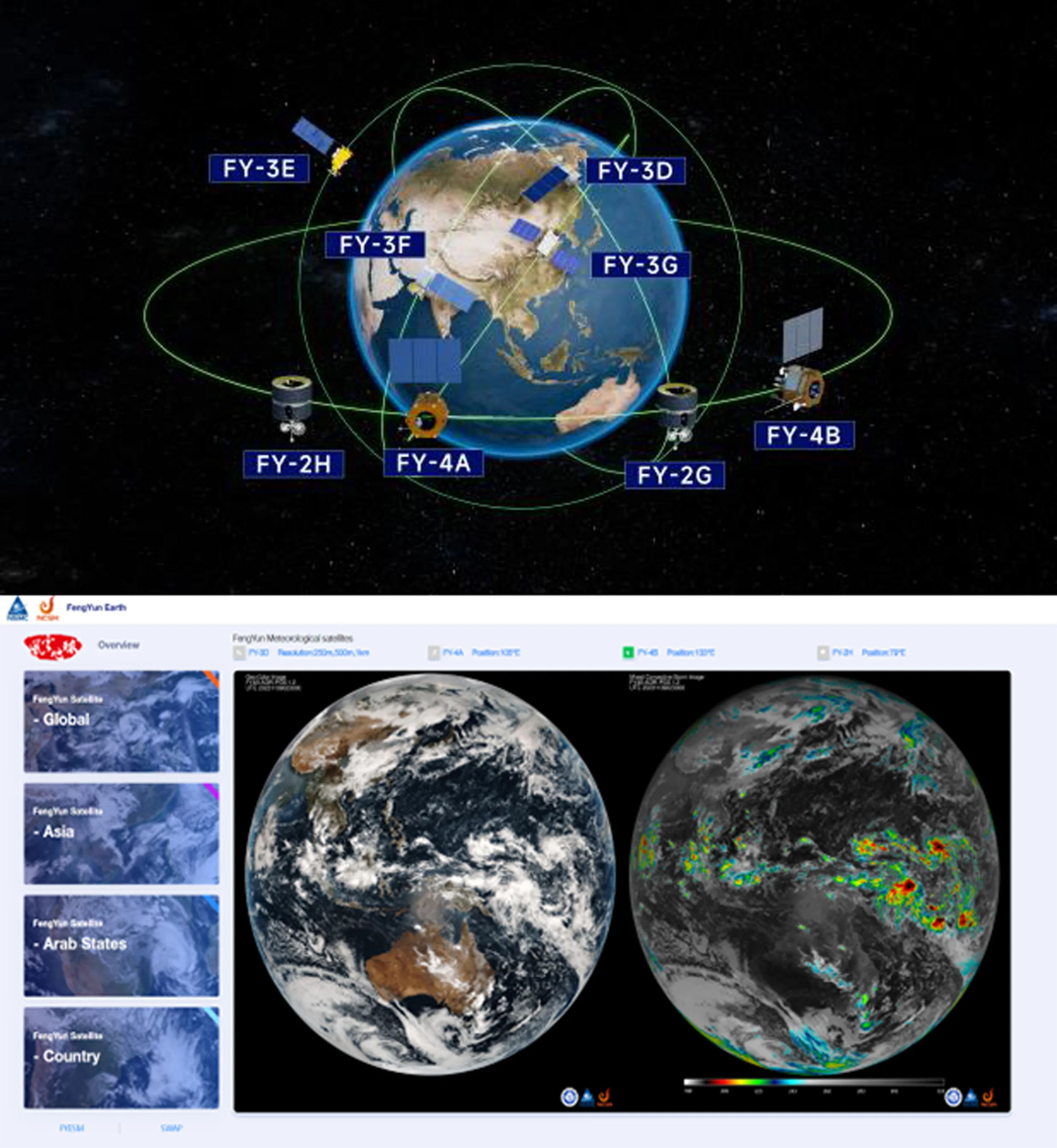
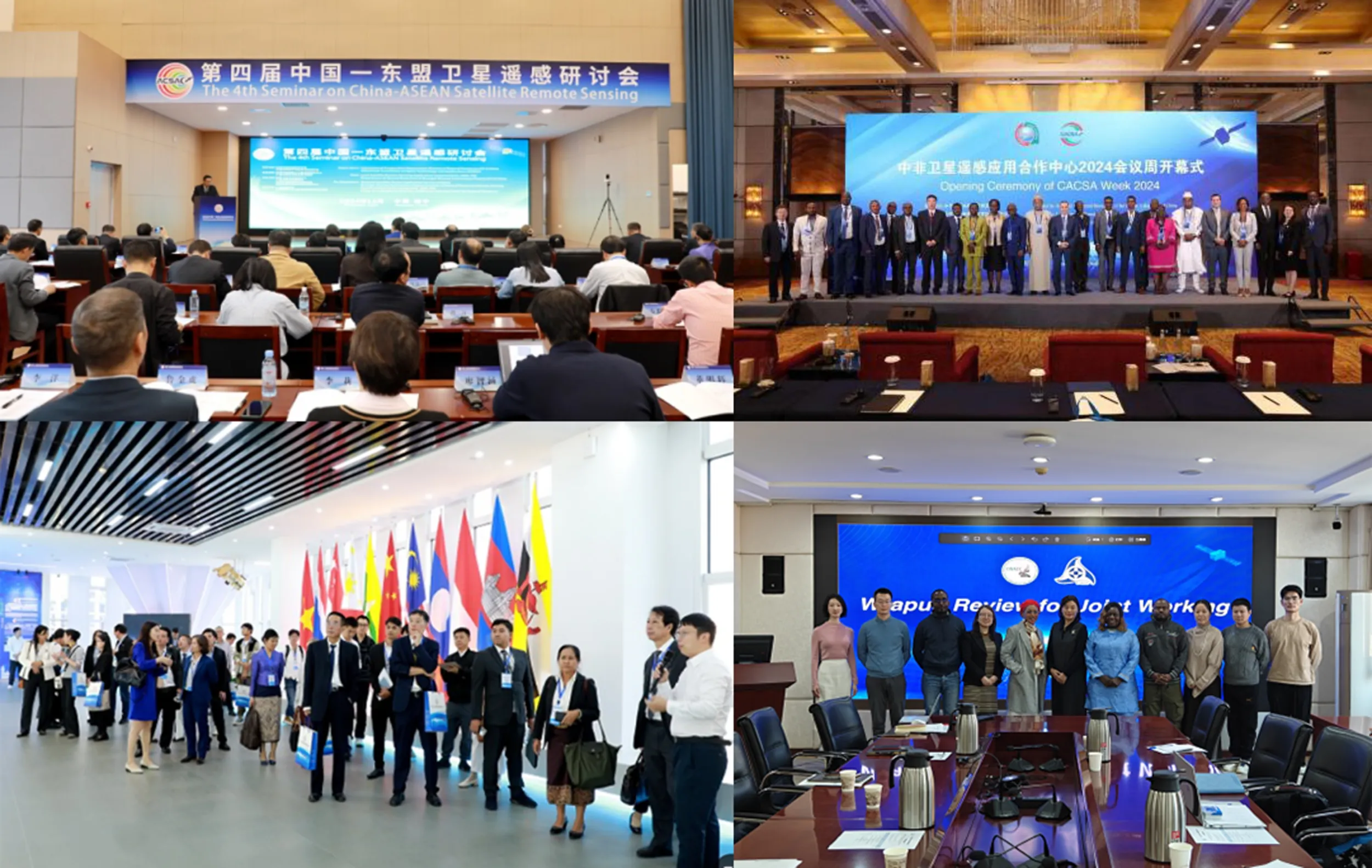
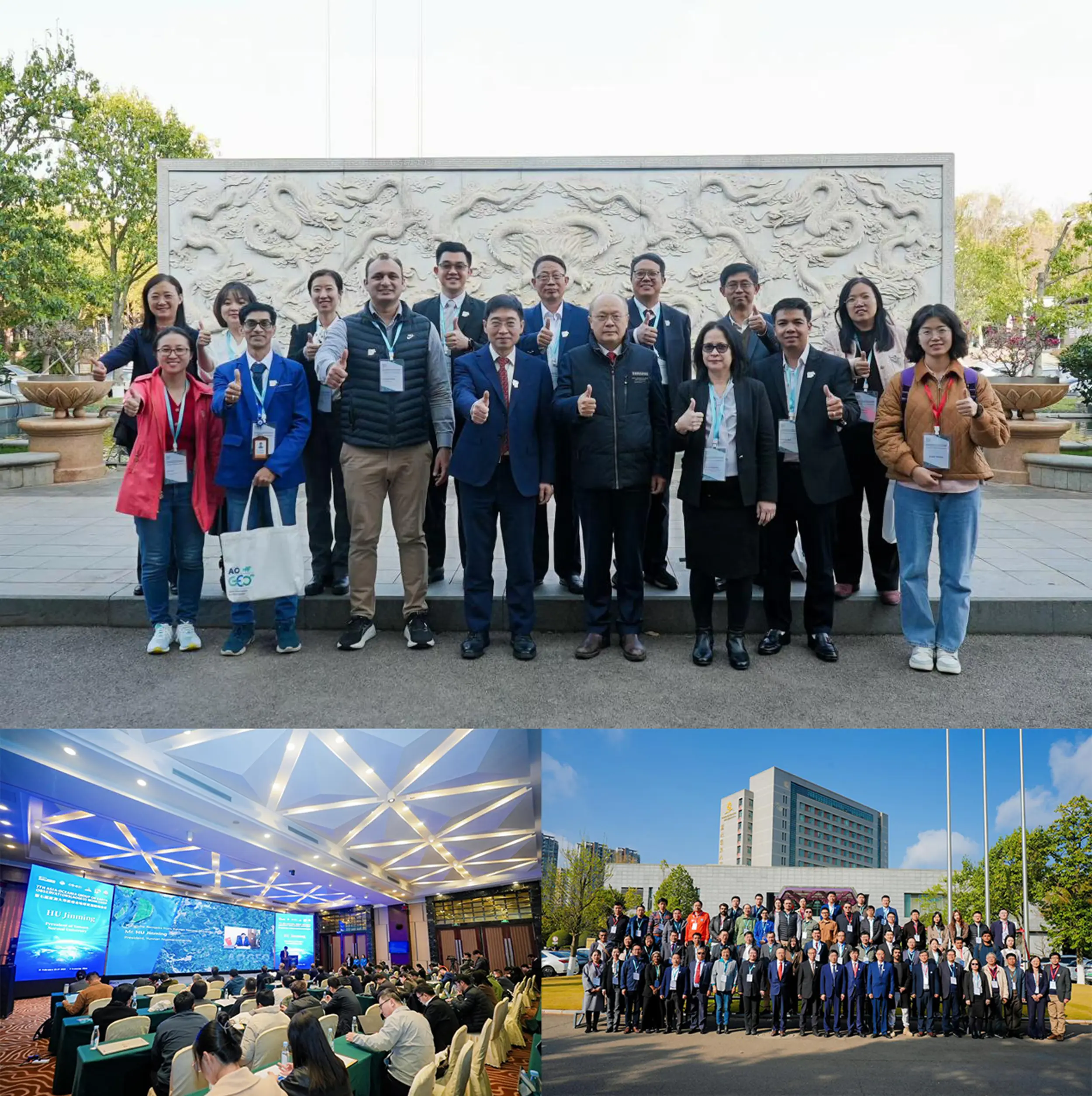
The 7th AOGEO (Asia-Oceania Group on Earth Observations) Workshop, with the theme of "Technology Advancement and Action of AOGEO for GEO Earth Intelligence Era", was held in Kunming China in February 2025. It brought together more than 80 participants from 14 countries (Japan, Australia, South Korea, Cambodia, Malaysia, Thailand, Vietnam, Laos, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Singapore, etc.) in Asia-Oceania region. More than 7900 people watched the broadcast through the through an open-access journal livestreaming platform in association with AIRCAS.

Xingfa GuAerospace Information Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences (AIRCAS) / Guangzhou University, China

SDGSAT-1 has obtained more than 400,000 scenes of global imagery data since its launch in 2021. Through the “SDGSAT-1 Open Science Program”, researchers from 104 countries have signed up to access the SDGSAT-1 data to conduct research and support informed decision-making related to sustainable development.
SDG Big Data Platform, the big data cloud service infrastructure platform for SDGs, has stored a total of 19.78 petabytes of earth science data, serving over 100 countries and regions worldwide.
Data products for sustainable development have also been developed and released. In 2024, for example, seven sets of African sustainable development data products were presented to Philemon Yang, president of the 79th session of the UN General Assembly, during the event themed “Global Development Initiative Supports the Global South -- China in Action,” held at the UN headquarters in New York.
The report series “Big Earth Data in Support of the Sustainable Development Goals”, drafted by the research team from the International Research Center of Big Data for Sustainable Development Goals (CBAS), have been released for six straight years. The 2023 edition was released at the High-level Meeting on Global Development Initiative Cooperation Outcomes held in New York. The latest report was launched on the UN website in September 2024.

Huadong GuoDirector General of International Research Center of Big Data for Sustainable Development Goals (CBAS) Professor of Aerospace Information Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences (AIRCAS)

With the support of GEO and its member community, we have enhanced the use of Earth Observation (EO) data to monitor the ecological environments of Pacific Island nations. In 2024, we released the "Remote Sensing Monitoring Report on the Ecological Environment in Pacific Island States (2024)", which reveals urbanization, coastline changes, and mangrove dynamics in Pacific Island nations since 2000. Additionally, we released individual remote sensing monitoring reports for 12 Pacific Island States, providing detailed analyses tailored to each state’s unique environmental conditions. Furthermore, we conducted an international training program for 26 participants from 15 Small Island Developing States (SIDS), strengthening their capabilities in marine and coastal ecological monitoring and disaster forecast. We also provided remote sensing emergency monitoring services for disasters such as earthquakes and landslides in Papua New Guinea and Vanuatu, with one report published on the SPREP website (https://pacific-data.sprep.org/dataset/vanuatu-earthquake-satellite-imagery-analysis-report). These initiatives have bolstered the resilience of Pacific Island nations to climate change through data-driven coastal management. For more information, please visit our website: https://resoc.sio.org.cn.

Huaguo ZhangDeputy Director of State Key Laboratory of Satellite Ocean Environment Dynamics, Second Institute of Oceanography, Ministry of Nature Recourse, China

National Disaster Reduction Center of China (NDRCC), as one of GEO Disaster Risk Reduction Working Group member agency, under the umbrella of GEO, actively engaged to facilitate to better using space-based technology for DRR, such as implementing a key R&D project for exploring the critical indicators and methodologies of Earth Observation applications under Sendai Framework, supporting UN-SPIDER Beijing Office for having held 10 years of annual Space-based Technologies for Disaster Risk Reduction Beijing Conference and providing satellite images and emergency mapping service for major disasters including the 2025 Myanmar Earth quake. Facing the GEO's Post-2025, we are willing to leverage increasing Chinese satellites for global disaster risk understanding, emergency response, S&T innovations.

SHI Feng Director General of National Disaster Reduction Center of China
Plan4all
Sustainability and biodiversity protection are at the heart of Plan4all’s mission. Through the GEO framework, we use open EO data to support land use decisions that work with nature—not against it.

Tomas MildorfChairman, Plan4all

KijaniSpace analytics will bolster GEOGLAM Crop Monitor, delivering timely EO intelligence that sharpens crop forecasts and strengthens food-security decisions.

Karel CharvatExecutive Board Member, Plan4all

With GEO’s inspiration and support, Plan4all has embraced GeoAI as a core approach to unlock actionable insights from EO and geospatial data. By making AI-powered tools openly available, we are helping communities and innovators drive sustainable change at the local level.

Karel CharvatExecutive Board Member, Plan4all


Secure World Foundation
“More than 11,200 active satellites currently orbit the Earth, providing tangible social, scientific, security, and economic benefits to billions of individuals all over the globe. Yet the ability to provide these important benefits from outer space is now threatened by a number of challenges. The Earth’s orbital space environment constitutes a finite resource that is being used by an increasing number of space actors.”
“Recognizing the rapid increase in the number of actors in outer space and the urgent need to promote norms of behavior and best practices to ensure sustainable activities in space, SWF is committed to facilitating dialogue, informing policy decisions, and fostering international cooperation in the peaceful uses of outer space.”

Peter MartinezExecutive Director, Secure World Foundation

Senegal
“The products developed through the SERVIR program are invaluable, providing us with near real-time, high-precision monitoring of our forest resources. As the forestry service welcomes a new generation of professionals, investing in capacity building is crucial to equip them with the skills needed to sustainably manage our ecosystems.”

Lieutenant Malick Diallo Directorate of Water, Forests, Hunting, and Soil Conservation (DEFCCS), Senegal; Member of the Multidisciplinary Working Group on Environment
"The establishment of the West African Regional Coastal Observatory represents a watershed moment in our approach to coastal management. By harnessing Earth Observation technologies, we've created a shared monitoring platform that transcends national boundaries, allowing us to track environmental changes with unprecedented precision. This geospatial framework not only helps us understand coastal vulnerabilities but transforms how we collaborate on solutions across the region."

Dr. Kako Nubukpo Commissioner in charge of the Department of Agriculture, Water Resources and the Environment, West African Economic and Monetary Union (UEMOA)

South Africa

Netherlands
Space for global development: education and capacity building
We are here to identify and understand vulnerability – and to convert it into resilience by developing, applying and sharing geospatial impact-driven solutions. We educate our students to be professionals, capable of acquiring knowledge and translating this into practical applications for solving real-world problems. Via our Geoversity platform we provide high-quality geospatial content and cutting-edge education. Legacy of the NSO Geodata for Agriculture and Water programme is included in this platform.

Freek Van Der MeerDean Faculty ITC, University of Twente

The role of Citizen Science
Our Action Research on Citizen Science helps GEO achieve impact related to sustainable development, elevating the value of citizen science communities and data from local to global scales. E.g. via empowering citizens in collaborative environmental compliance assurance in the EC More4Nature project.

Uta WehnProfessor of Citizen Science and Sustainability, IHE Delft Institute for Water Education, Leiden University

More effective use of water in agriculture on a global scale
An increasing number of countries does not have enough water to grow food for their growing population. More crop per drop is needed. This is why the Netherlands supports the FAO WaPOR program since 2014. WaPOR has the aim to improve land and water productivity in the face of climate change. Since October 6 2023 FAO WaPOR data are available at a global scale. Almost hunderd use cases are documented.

Aart van der Horst Department of Inclusive Green Growth, Ministry of Foreign Affairs, the Netherlands
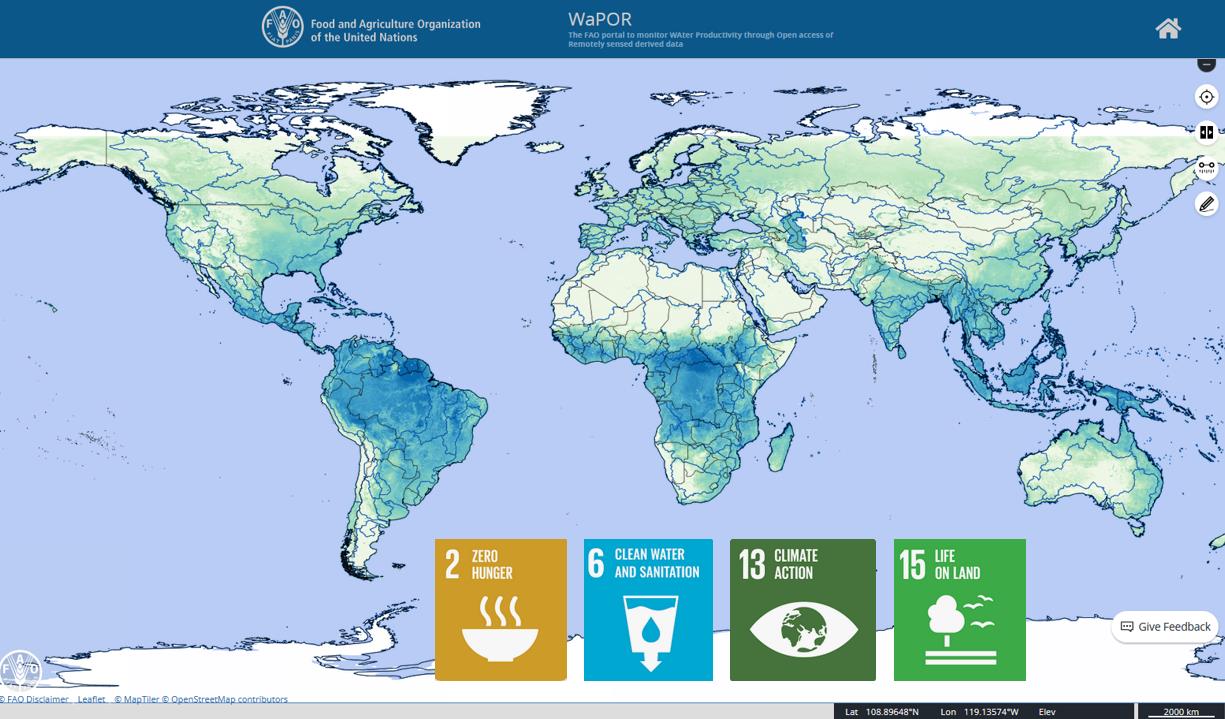
Space applications for society, science and economy
Space for climate and living environment is one of the missions of the long term the Netherlands Strategic Agenda for Space (January 2024). The Netherlands actively stimulates the development and use of services based on satellite data, to bring the benefits of space to society, science and economy.

Harm van de WeteringDirector, GEO Principal for the Netherlands, Netherlands Space Office (NSO)

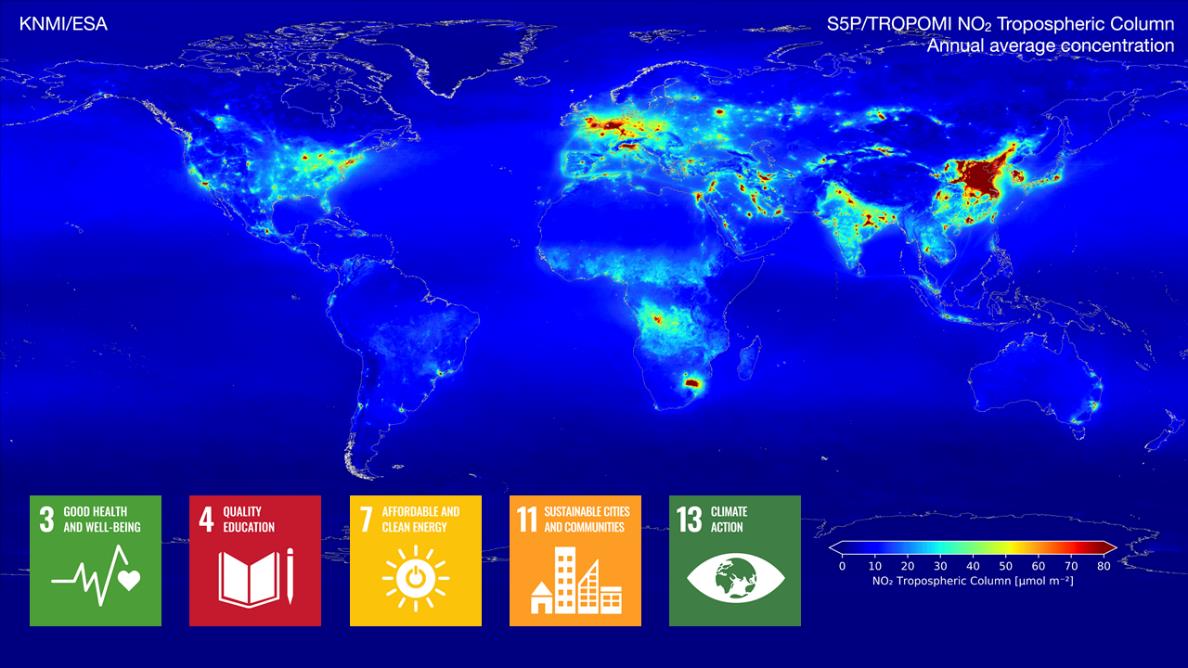
Seven years global view on air pollution and greenhouse gasses
The TROPOMI instrument (on Copernicus Sentinel-5P) provides timely images of air quality and climate parameters for every place of the Earth. TROPOMI data is used for air quality forecasts and to monitor which policy measures are effective for improving the air quality. TROPOMI has also been very successful in tracing methane emissions from oil and gas industry, urban hotspots (garbage dumps) and landfills. For instance, TROPOMI data is included in the International Methane Emissions Observatory (IMEO).

Pepijn VeefkindPrincipal scientist TROPOMI, Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute (KNMI)
Towards a better food security
Over 4.5 million smallholder farmers in Africa and Asia have benefitted from products and services based on open and free satellite data in the Geodata for Agriculture and Water (G4AW) programme. Geodata-based services assist farmers and pastoralists in increasing their productivity and adapting to climate change. The successes, challenges and lessons learned of the 25 initiatives of G4AW are shared on the G4AW website. G4AW services are also introduced and scaled in new countries.

Wilma van Esch Department of Inclusive Green Growth, Ministry of Foreign Affairs, the Netherlands

The time for climate action is now
We can turn the tide if we take fast, decisive action. The world needs to adapt to what is coming and do everything possible to immediately reduce emissions. Availability and accessibility of reliable data is crucial in this endeavor. Earth observation plays an important role. It increases our understanding of the consequences of climate change, and can thereby be a powerful tool for policymakers across the world.

Jaime de Bourbon de Parme Climate Envoy, Kingdom of the Netherlands
Netherlands Space Solutions for Climate Adaption and Mitigation
Netherlands Space provides support to education, science and innovation. Dutch companies and institutions develop new innovative solutions using satellite data that contribute to the provision of information to facilitate climate adaptation and mitigation.

Kathelijne BeenenAdvisor Satellite Applications, Netherlands Space Office (NSO)

Space solutions contribute to peace and security
The Dutch initiated the Water, Peace and Security initiative - a broad coalition of international partners coordinated by IHE Delft Institute for Water Education - designed innovative tools and services identifying water-related security risks to help mobilize stakeholders, build capacity and facilitate action. Understand - mobilize - learn - facilitate - act!

Eva Schreuder Department of Inclusive Green Growth, Ministry of Foreign Affairs, the Netherlands

Objective information in support of sustainable sourcing landscapes
Geodata are used in decision making in agriculture, landscape, climate, and water for planning, monitoring and reporting of localized interventions. Geodata are used in support of the EUDR regulation and by the Verified Sourcing Areas (VSA) of the Sustainable Trade Initiative (IDH) and partners to verify outcomes at landscape level. Doing this, spatial data are used by local stakeholders, including government and private sector, driving sustainable production and international partners, like retailers and brands, for sustainable sourcing.

Albert Schenk Department of Inclusive Green Growth, Ministry of Foreign Affairs, the Netherlands


United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change

Ukraine

Vietnam
“VietNam has been a member of the Executive Committee of the GEO Global Agricultural Monitoring Initiative (GEOGLAM ExCom) since 2019. In this role, we have assisted in the development and execution of implementation plans. As a nation heavily reliant on rice production, VietNam has leveraged GEOGLAM to improve crop forecasting, resource management, and food security, delivering benefits not only domestically but also to Asia and beyond. In the meantime, VietNam keeps playing a pivotal role in the CH4Rice project, an initiative under Asia-RiCE within GEOGLAM. This work underscores our dedication to applying Earth observations for sustainability”.

Tuan PhamDirector General, Vietnam National Space Center, Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology, Principal Alternate Representative to the Group on Earth Observations

Caribbean Meteorological Organization
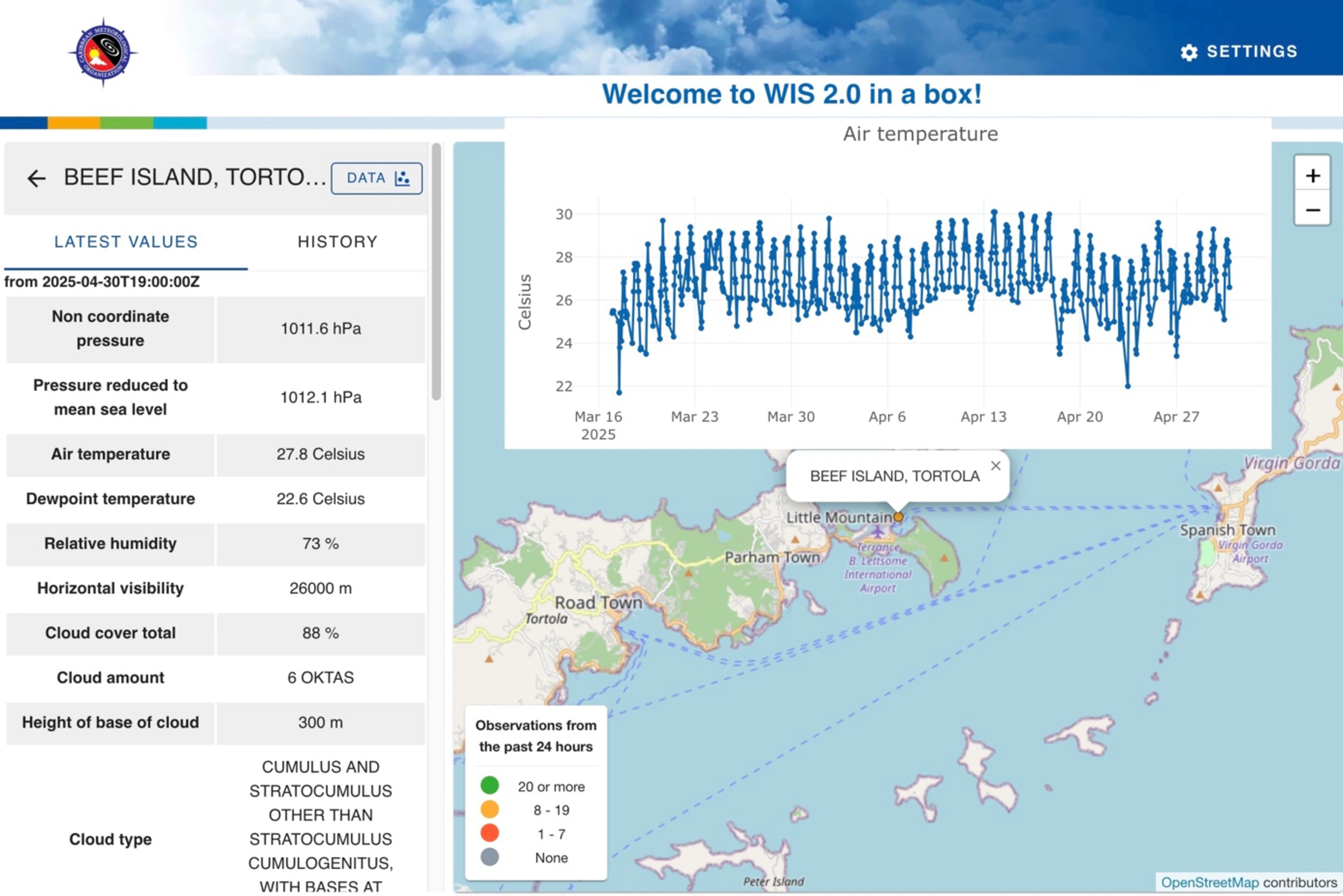
“Encouraged by GEO and the GEO Member Community, the Caribbean Meteorological Organization (CMO) Headquarters has implemented a WIS 2.0 node that is a powerful scientific tool facilitating and supporting the continuous collection, analysis, and exchange of weather and climate data taken at a local ground level to better understand microclimates and underpin early warnings in 16 Caribbean countries.”

Arlene LaingCoordinating Director, Caribbean Meteorological Organization, Headquarters Unit

European Union
European Commission, Directorate General for Defence Industry and Space.
Unit DEFIS.D.3.
Copernicus has revolutionized Earth observation, addressing key societal priorities such as environmental monitoring, climate change, and disaster management. Copernicus free, full, and open data foster a culture of innovation and enables policymakers and the public to make informed decisions. As such, Copernicus represents a major contribution to GEO and broader Sustainable Development Goals.

Mauro FacchiniHead of Unit, Earth Observation, Directorate General for Defence Industry and Space, European Commission
European Commission, Directorate General for Defence Industry and Space.
Unit DEFIS.C.3.
“Copernicus free and open powers a wide range of downstream services and plays a key role in advancing the global Earth observation ecosystem and supporting GEO’s objectives. It has spurred innovation and economic growth, fostering a vibrant European space economy and a dynamic downstream sector, translating space data into real-world impact”.

Jolanda Van EijndthovenHead of Unit, Space Economy, Directorate General for Defence Industry and Space, European Commission
European Commission’s Directorate General for International Partnerships.
"The Africa-EU Space Partnership Programme, a Global Gateway flagship initiative, represents a pivotal step in strengthening the ties between Europe and Africa, leveraging the power of space technologies to drive sustainable development, enhance climate resilience, and foster innovation. Through this collaboration, we are not only advancing Africa's green and digital transition but also empowering its private sector and institutions to shape a more resilient society."

Carla MontesiDirector for Green Deal and Digital Agenda at the European Commission’s Directorate General for International Partnerships.

European Commission, Joint Research Centre. “As we enter the third decade of the work of the Group on Earth Observations, our common global focus is on evolving existing Earth Observation products and services to Earth Intelligence, recognizing the critical role that this transformation will play in addressing the world's most pressing challenges, such as climate change and sustainable development. The European Commission’s Joint Research Centre, in collaboration with international partners and stakeholders, fully embraces this. We increasingly see in our work supporting the policy needs of European Union for Earth Observation and the multilateral UN system, that Earth Observation can only reach its full potential if it is combined and integrated with other sources of data, providing actionable intelligence that can help drive policy coherence. We are convinced that the next decade of GEO will be a transformative period for how Earth Observations impact policy, decision-making, and the lives of citizens worldwide, fostering a more sustainable, equitable, and resilient future for all.

Alessandra ZAMPIERIDirector of the Directorate for Sustainable Resources, European Commission, Joint Research Centre (JRC), Italy

European Environment Agency (EEA). “The European Environment Agency (EEA) recognises the importance and significant value of the GEO community and is committed to continuing its efforts to enhance the sharing and use of Earth observation data in support of environmental and climate policies. Funded by the European Commission (DG RTD), the EEA launched in 2024 a second three-year project, “Enhancing the access to in situ Earth observation data in support of climate change adaptation policies and activities”. Through this initiative, the EEA is actively engaged in GEO and EuroGEO data sharing activities.
Within this context, the EEA contributes to the GEO Data and Knowledge Working Group, promoting open data sharing and sound data management practices across the Earth observation community. We have supported the development of GEO success stories that demonstrate the value of implementing open data principles and we are actively contributing to the formulation of the post-2025 GEO In-Situ Data Strategy.
In addition, the EEA is developing and maintaining the Geospatial In-situ Requirements Database (G-reqs), a tool to document and manage in situ data user needs across the GEO Work Programme. This work builds on our role as coordinator of the Copernicus In-Situ Component. We will soon begin engaging with in-situ data providers to help align identified needs with available data sources. These efforts aim to enhance the availability and accessibility of in-situ data, furthering the GEO vision of Earth Intelligence.
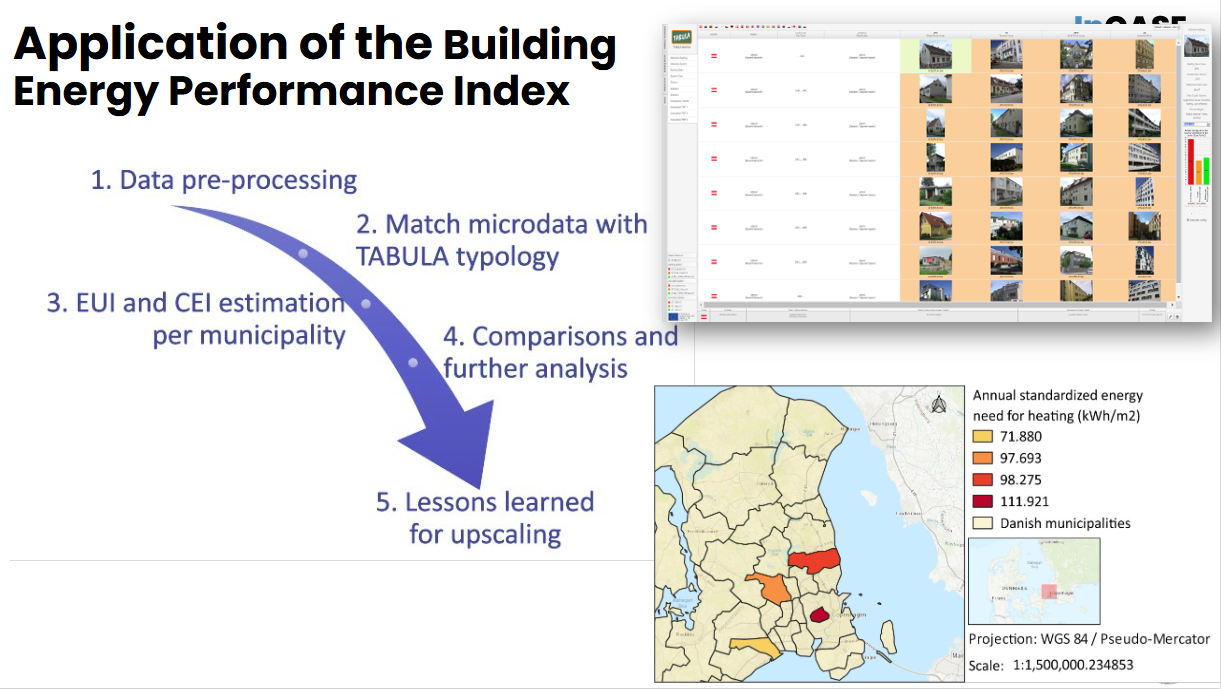
The project also includes the development of practical showcases illustrating how openly available in-situ datasets can support climate adaptation policies. For example, we have developed a methodology that combines building level microdata, provided by local authorities with national residential building typologies (extracted from the TABULA webtool) to calculate a Building Energy Performance Index at municipal level, with an initial application in Denmark.
As one of the EU agencies entrusted with the implementation of the Copernicus component of the EU Space Programme —specifically the pan-European products of the Copernicus Land Monitoring Service (CLMS) and coordination of the Copernicus In-Situ Component— EEA sees the role of the GEO community as key. GEO initiatives can leverage CLMS products, know-how and expertise to achieve their objectives. At the same time, GEO offers a unique platform to connect with key in-situ partners and to promote open data and open observation principles on a global scale”.

Karl HamiltonHead of Digital Department and GEO Principal, EEA, Denmark
Horizon Europe Project EuroGEO Secretariat (EuroGEOSec). The EuroGEOSec project develops a fully operational and sustainable EuroGEO Secretariat contributing to the Regional initiative EuroGEO.
EuroGEO promotes, showcases and stimulates Combination, Coordination and Cooperation to serve European and international policies and users through Earth Intelligence leveraging European excellence by:
● Actively stimulating and monitoring the European contribution to GEO and increasing GEO benefits for Europe,
● Acting as a Coordination forum for European and national initiatives relevant to both the GEO work programme and European priorities.
● Addressing the significant gap between policy needs, end-user requirements, and technology providers
● Ensuring a broad participation of both demand and solution providers, leveraging the entire Copernicus value chain and user community, the private sector, and platforms/twins/infrastructures within its Action Groups.
● Supporting Action Groups mobilised as agents of change

Thierry RanchinDirector of the Centre Observation, Impacts, Energie from MINES Paris – PSL, France and Scientific coordinator of the EuroGEOSec Project

Horizon Europe Project Arctic PASSION. Comprehensive Arctic observing is needed more than ever with the rapid pace of local climate change. Arctic PASSION has taken great effort to involve Indigenous communities and local people with researchers in observation making and reaping benefits from the related EO services.

Alfred Wegener Institute, Germany, Coordinator Arctic PASSION
Horizon Europe Project EO4EU. “EO4EU Unleashes the potential of Earth observation data through AI and extended reality—empowering everyone to explore, analyse, and act.”
EO4EU has an easy-to-use interface including personalized dashboards, a smart search engine and data visualization, analysis and interpretation. Users can also write their own code and execute it serverless with minimum effort. Finally, EO4EU provides an immersive experience with its augmented and extended reality interface.
The EO4EU project has made an invaluable contribution to FAIRifying EO data with its one-stop shop that facilitates finding, accessing and reusing EO data and analyses (https://bit.ly/4h6vvDk). It significantly contributes to advancing environmental knowledge at local and EU levels.

Stathes Hadjiefthymiades National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Greece, project coordinator

Horizon Europe Project Open-Earth-Monitor (OEMC). “In a world of AI technology exceeding our best experts and replacing jobs at a rapid pace, it is crucial to have transparent processes, models trained using FAIR (open findable accessible interoperable and reusable data). This can be best achieved by using and enabling open source software and open data, i.e. by supporting and enabling open development communities, especially in the field of Earth Observation and spatial data science.
OEMC embraces the use and extension of open-source software, open reproducible procedures and data sharing. Building on several existing platforms, such as Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem and data from the European Environmental Agency, users can improve existing data and services and develop their own.
OEMC also produced several new data sets, such as land degradation hot spots supporting the United Nations’ Convention to Combat Desertification, or datasets used to map drivers of deforestation across Africa. Also developed a computational framework employed to produce cloud-free, data sets with applications including land cover analysis and crop-type mapping.
OEMC currently has more than 20 monitors with pilot use cases such as the ‘World drought monitor’, ‘EU biodiversity monitor’ and ‘Tropical deforestation monitor’ (Ethiopia) in which users are at the centre of monitors’ design, and applications are often developed in close collaboration. Use cases are currently uploaded to the GEO’s Knowledge Hub.”

Tomislav HenglDirector OpenGeoHub foundation, The Netherlands
Horizon Europe Project Urban Data Space for Green Deal (USAGE). “In the project USAGE we are paving the way to create urban data spaces that focus on problems identified in the Green Deal. Notably, we use open EO data to characterize urban heat islands, and combine such data with other data sources to determine how they affect population in urban areas”

Oscar CorchoFull professor, Universidad Politécnica de Madrid, Spain

Integrated Carbon Observation System
“ICOS and the European Space Agency (ESA) are exploring opportunities to join forces to combine in situ and satellite measurements for calibration/validation (cal/val) activities, to ensure the accuracy, reliability and consistency of satellite data. ESA currently funds cal/val campaigns, but ICOS data gives ESA the benefit of using near-real-time, long-time series and quality-controlled intercomparable measurements at several locations in Europe and beyond. ICOS is also ready to improve the routine measurements in order to match satellite requirements – a gap analysis is currently underway in the framework of the New Users for a Better ICOS (NUBICOS) project.”

Elena SaltikoffHead of Operations & Coordinator of the NUBICOS project
“Ocean CO₂ uptake varies significantly in time and space and needs a network of high-quality continuous measurements to monitor and predict these variations. The ICOS ocean stations, along with other merchant and research vessels, moorings, sail boats and uncrewed surface vehicles, are the background of the Surface Ocean CO₂ Observing Network (SOCONET). It is the corner stone of a value chain that delivers data, e.g. to the community-driven data quality control and synthesis element known as the Surface Ocean CO₂ Atlas (SOCAT), which is, in turn, used for global decision-making. The alarming decline in ocean CO2 observations in recent years underlines the role of ICOS in supporting the surface ocean carbon value chain.”

Sindu Raj ParampilScientific Integration Officer
“With the Knowledge and Climate Services from an African Observation and Data Research Infrastructure (KADI) project, ICOS intensifies its cooperation with Africa. The GEO Post-2025 Strategy’s emphasis on co-design, digital infrastructure, open and FAIR data echoes the core values of KADI. ICOS is committed to ensuring that African-led knowledge systems are central to the next generation of EO services. At the Climate Chance Europe-Africa Summit in Marseille (April 2025), KADI presented its deeply collaborative activities, aiming to shift the center of gravity of climate research toward African ownership, leadership, and innovation.”

Theresia BilolaProject manager of the KADI project

“The EU has established a certification framework for permanent carbon removals and carbon farming (CRCF regulation). In the Integrated Research Infrastructure Services for Climate Change Risks (IRISCC) project, ICOS has, together with various stakeholders, categorized risks related to carbon farming and possible certification schemes. These risks can add up and severely reduce the potential of measures initially taken to enhance carbon sequestration. The work highlights the need for digital tools providing monitoring capabilities and common, openly available data sets able to assess the schemes. ICOS is ready to contribute to such a data pool, e.g. with in situ flux data benchmarking models and supporting their improvement.”

Werner KutschDirector-General of ICOS ERIC


International Astronautical Federation
“The IAF announces that it is organizing a second edition of its IAF Global Space Conference on Climate Change (GLOC 2026) in Kigali, Rwanda, on 2-4 June 2026. The IAF looks forward to continuing the conversation on several of the topics addressed during the GEO Global Forum at the GLOC 2026.”

Gabriella ArrigoIncoming President, International Astronautical Federation (IAF)


International Society for Digital Earth
"The International Society for Digital Earth (ISDE) is proud to work alongside GEO in advancing the next generation of Earth Intelligence. Through the development of Digital Earth technologies and thought leadership — including our flagship publications, the International Journal of Digital Earth and the Big Earth Data journal, as well as the foundational vision outlined in Digital Earth: Yesterday, Today and Tomorrow — Our joint collaboratuion with GEO has been strengthened by ISDE being now member of the GEO Programme Board. In this Geo Forum ISDE is initiating in joint cooperation with GEO, a GEO Digital Earth Conveners initiative. ISDE empowers global efforts to integrate Earth observation, geospatial data, and artificial intelligence. By promoting open knowledge, innovation, and collaboration through its journals and international symposia, ISDE helps realize GEO’s mission to build a more informed, resilient, and sustainable world."

Alessandro AnnoniPresident, ISDE


Korea, Republic of

Space for Climate Observatory
United Kingdom

Mercator Ocean International
The Ocean is undergoing dramatic changes due to climate change, pollution and the over-exploitation of marine resources. More than ever, advanced ocean monitoring and prediction activities are needed. With its leading role in GEO Blue Planet and in the EU Copernicus Marine Service and Digital Twin Ocean, Mercator Ocean International has developed ocean intelligence capabilities for sustainable ocean management that are fully aligned with the GEO vision

Pierre BahurelDirector General

World Data System
Consistent with GEO’s vision for trusted and accessible Earth Intelligence, the World Data System (WDS) seeks to enhance the capabilities, impact, and sustainability of trusted data repositories, and advocates for accessible data and transparent and reproducible science. Earth science disciplinary data repositories are strongly represented within the WDS, and adhere to its data sharing principles.

Reyna BroadhurstAssociate Director, International Technology Office, World Data System


Ecuador
“GEO Tierra Ecuador, inspired by the initiatives of GEO and its community, promotes the use of Earth Observation (EO) data to strengthen geospatial analysis, data sharing, and regional cooperation. Coordinated by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and the Military Geographic Institute, the group has formed national teams in six key areas: biodiversity, disaster resilience, food security, health, water resources, and security for development.
Our network has been instrumental in responding to recent emergencies—such as landslides, floods, and oil spills—enabling rapid assessments, informed decisions, and effective action. Thanks to GEO's support, we have strengthened the international exchange of knowledge and capabilities.
Ecuador reaffirms its commitment to regional cooperation through open data policies, the use of interoperable geospatial information, and innovative solutions for more sustainable and resilient development”

Manuel Iván Ramírez AlvarezDirector, INSTITUTO GEOGRÁFICO MILITAR, ECUADOR
