Italy
- Home/
- Partners/
- Member Governments/
- Italy


Italy is strengthening the coordination amongst national experts involved in Earth Observation (EO) domains through the GEO-ITALY Group (www.geoitaly.org). The GEO-ITALY overarching goal is to reinforce the synergies amongst involved institutions in Italy, thus facilitating a broad range of capacity building and outreaching activities to stakeholders and policy makers both at national and international level. Members of GEO-ITALY are Representatives of the Ministry of Environment and Energy Security and and scientists, researchers and managers employed in several Institutes of the National Research Council of Italy, in the National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology (INGV), in the Italian National Institute for Environmental Protection and Research (ISPRA), in many other public institutions in the Country, such as the Italian Space Agency (ASI) and the Euro-Mediterranean Center on Climate Change (CMCC), as well as in private companies such as PLANETEK and e-GEOS.


The Global Observing System for Mercury (GOS4M) Flagship main challenge is to foster the sharing of monitoring data and modelling tools to support the policy implementation. GOS4M (www.gos4m.org) is aimed to federate existing networks, monitoring programmes and observing infrastructures – currently it provides a link to the Global Mercury Observation System (GMOS – www.gmos.eu) and major existing regional networks. During the last year GOS4M developed the Knowledge Hub aimed to support the achievement of the objectives of international programmes and conventions related to mercury pollution which include UNEP, Minamata Convention on Mercury (MCM) Secretariat, UNECE-LRTAP and 2030 UN Agenda on SD. Special attention is paid to support all interested Parties in the implementation of the MCM. To this end global comparable monitoring data, validated models and policy interoperable tools are provided as part of the GOS4M Knowledge Hub designed to evaluate the relationship between cause and impact of mercury contamination, analyse cost-effective strategies aiming ot reduce the mercury contamination at regional and global scale and co-design policy scenarios aiming to achieve the target of the MCM. GOS4M is contributing to the GEO Knowledge Hub.


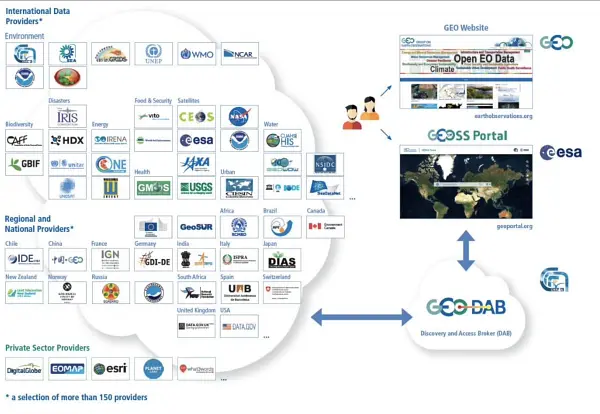
Italy is continuing its activity aiming to improve discovery and access to data, information and knowledge and to support and further develop the GEOSS Platform as an open and public global infrastructure for data sharing and knowledge generation. Italy continues operating and advancing the GEO Discovery and Access Broker (GEO DAB) framework as one of the key components of the GEOSS Platform. Italy carries out activities for knowledge generation and management developing the Virtual Earth Laboratory (VLab), a knowledge platform for model sharing and running in multicloud environments. Italy is co- chair of the GEOSS Platform Operation Team (GPOT) and member of the GEO Infrastructure Development Task Team (GIDTT). It also participate to the activity aof the GEO Data Working Group and its soub-groups. For the advancement and utilization of the GEOSS Platform, collaborations are ongoing with ESA, EC-JRC, USA (USGS), Germany (DWD), Switzerland (University of Geneva), China (Ministry of Science and Technology), Chile (Ministerio de Bienes Nacionales).


The Paris Agreement is one of the three GEO Engagement Priorities. To achieve its targets, systematic and long-term earth observation data are needed, in order to: improve carbon budgets, reduce uncertainties of national inventories, and provide decision makers with reliable information. Italy is supporting, by co-leading the secretariat, the GEO Carbon and GHG Initiative, which has the objective of developing an operational global observing system for monitoring and evaluating changes in the carbon cycle and GHG emissions. Furthermore, through a dedicated activity within the H2020 project VERIFY, Italy (CMCC), is contributing in creating the links between the “Observation-based system for monitoring and verification of greenhouse gases” foreseen by the project and GEO, ensuring the coordination with global data synthesis efforts.


As a further Italian contribution to GEO, GEO Mountains (www.geomountains.org/) aims to connect and facilitate access to diverse sources of mountain observations and information regarding drivers, conditions and trends in biophysical and socio-economic processes of change, at different scales. GEO Mountains advances our capacity to combine data on mountains to meet emerging scientific and policy knowledge needs, thereby 1) enhancing our understanding of processes of global change in mountain regions, 2) improve our ability to provide policy and investment relevant advice, and 3) assess SDGs in mountain areas.


A further contribution of Italy to the many GEOSS Ecosystems tasks is offered by the GEO ECO (GEO Global Ecosystem) Community Activity and Action Group, co-lead by CNR. GEO ECO builds up and extends the approach used in the European Horizon 2020 ECOPOTENTIAL project, led by CNR, and from a few other initiatives, to other protected areas in Europe and in other continents. GEO ECO aims to use available Earth Observation data, research results and tools on a global scale for enhancing knowledge on natural ecosystems, identifying protected areas (PAs) of international relevance as focus areas for its activities, as they are aimed to preserve natural ecosystems, and thus have a high intrinsic value for human societies. In Italy, a key PA will be the Gran Paradiso and the Alta Murgia National Parks, also involved in ECOPOTENTIAL, the former H2020 project on Earth Observation data for ecosystems in protected areas supporting GEO (2015-2019). The detection and modelling of the state and development of natural ecosystems in PAs is a priority for the monitoring the advancement of the SDG 14 and 15. It also extends its analysis to unprotected areas. GEO ECO is adopting the view of ecosystems as "one physical system" with their environment, characterized by strong geosphere-biosphere-anthroposphere interactions across multiple space and time scales. The GEO ECO implementation plan can be downloaded here: www.earthobservations.org/documents/gwp20_22/GEO-ECO.pdf


A further contribution of Italy to the many GEOSS Ecosystems tasks is offered by the GEO ECO (GEO Global Ecosystem) Community Activity and Action Group, co-lead by CNR. GEO ECO builds up and extends the approach used in the European Horizon 2020 ECOPOTENTIAL project, led by CNR, and from a few other initiatives, to other protected areas in Europe and in other continents. GEO ECO aims to use available Earth Observation data, research results and tools on a global scale for enhancing knowledge on natural ecosystems, identifying protected areas (PAs) of international relevance as focus areas for its activities, as they are aimed to preserve natural ecosystems, and thus have a high intrinsic value for human societies. In Italy, a key PA will be the Gran Paradiso and the Alta Murgia National Parks, also involved in ECOPOTENTIAL, the former H2020 project on Earth Observation data for ecosystems in protected areas supporting GEO (2015-2019). The detection and modelling of the state and development of natural ecosystems in PAs is a priority for the monitoring the advancement of the SDG 14 and 15. It also extends its analysis to unprotected areas. GEO ECO is adopting the view of ecosystems as "one physical system" with their environment, characterized by strong geosphere-biosphere-anthroposphere interactions across multiple space and time scales. The GEO ECO implementation plan can be downloaded here: www.earthobservations.org/documents/gwp20_22/GEO-ECO.pdf


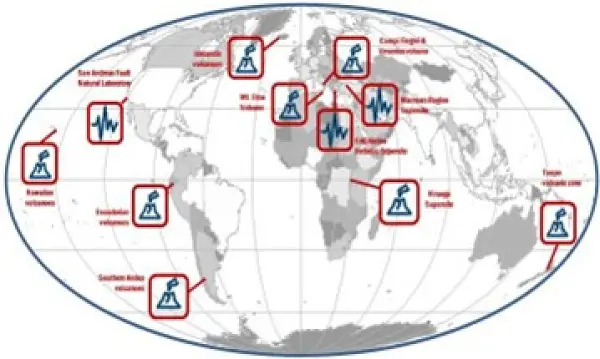
The Italian Space Agency (ASI) actively supports GEO Initiatives related to Disasters Risk Reduction like GEO-GSNL and GEO-DARMA. ASI regularly provides thousands products from its national asssets (mainly COSMO-SlyMed, but also PRISMA and SAOCOM over ASI Area of Interest) to all the 13 Supersites and Natural laboratories all over the world and to pilot projects whose purpose is to demonstrate the value of earth observation data for Disaster Risk Reduction and to build regional capacity in this sector.


Italy, through the INGV, coordinates and supports with important in-kind resource, the GEO-Geohazard Supersites and Natural Laboratories initiative (GEO-GSNL), established in 2010 under the Disaster SBA. GSNL is a network of 11 Supersites where a large community of scientists works to generate products for science-based decision making in Disaster Risk Management. GSNL is supported by the CEOS space agencies with satellite imagery and by a number of local monitoring agencies with in situ data. Supersite scientists openly share their in-situ and satellite data, promoting an Open Science approach and focusing on the sharing of scientific knowledge, capacity development, and technological innovation to increase the societal benefit geohazard science. All the Supersite coordinators are authoritative actors in the national frameworks for disaster prevention and response, and as such they constantly deliver hazard information generated for the Supersite, to the national decision makers, ensuring rapid and direct societal benefit of scientific findings. The Italian Space Agency (ASI) also supports GEO-GSNL, providing, on a continuous basis, over 2500 COSMO-SkyMed products per year that are key for achieving the GSNL objectives.

The Italian Space Agency (ASI) has launched on 22 March 2019 the PRISMA satellite carrying an hyperspectral sensor with a Ground Sampling Distance (GSD) of 30 m and covering the wavelength range from 400 nm to 2500 nm, with 10 nm spectral sampling. The launch was successful and the in-orbit commissioning has been completed, allowing PRISMA data to be accessible since May 2020 through the dedicated portal https://prisma.asi.it/. Data policy is based on a quasi-open and free access, with limitations on products per user quantities and on priorities for acquisition requests conflicts solving, to cope with the operational capabilities of the mission. Data policy allows commercial exploitation of value added product/services still delivering free of charge but forbids PRISMA original data redistribution.


Italy is supporting GEO and UN-Habitat “Earth Observation Toolkit for Sustainable Cities and Human Settlements” Programme. The Programme participates to the EO4SDG Initiative and aims at developing a customizable and continually updated toolkit on the integration of Earth Observation and geospatial information into the urban monitoring and reporting processes on SDG targets and indicators based on inputs from UN Member States and cities. The CNR-IIA indicator estimation approach consists of deriving and updating, from Earth Observation data, some essential variables for the urban ecosystem: the spatial distribution and density of urban population and settlement maps. By integrating these essential variables with other domain- specific information i.e., the particle pollutant maps, specific urban resilience indicators and sub-indicators can be quantified. The case study focuses on updating the distribution map of the migrant population regularly residing in Bari and neighboring municipalities to monitor progress on the inclusiveness and sustainable urbanization targets of the SDG 11 of the UN 2030 Agenda.


The Italian National Copernicus User Forum reflects the procedure of the Copernicus User Forum. It is composed by representatives of user communities belonging to public institution, public and private research bodies, industries and enterprises, covering all the Copernicus domains. Each User Community representative participating to the activities has to stimulate the community that represents, from central to local level, by promoting the use of Copernicus services and products and to link existing national EO initiatives.


Another Italian contribution to GEOSS, namely to AfriGEOSS, is represented by the EC Project PanAfGeo (Phase II) PanAfGeo - Pan-African Support to the EuroGeoSurveys-Organisation of African Geological Surveys (EGS-OAGS Partnership), co-funded by DG-DEVCO, is a project which supports the training of geoscientific staff from African Geological Surveys through the development of an innovative training programme. The project aims to increase African-owned geological knowledge and skills for sustainable mineral exploitation and related infrastructures, and natural disaster prevention and mitigation. Specifically, PanAfGeo enhances the capacity and role of African national Geological Surveys; • Contributing to mineral resource assessments by national Geological Surveys in Africa; • Increasing the activity of national Geological Surveys in regional mapping and exploration to upgrade their geoscientific information base and mineral inventories; • Strengthening the level of geological knowledge and skills in national Geological Surveys through training; • Strengthening OAGS’ potential to meet the needs of the African continent. Capacity building is addressed to over 1,200 trainees (mostly African geologists) with the organization of 49 short- and medium-term trainings in several African countries focused on wide range of geosciences topics such as satellite imagery analysis, geological mapping through GIS techniques, geo-hazards geochemistry and analytical chemistry, economic geology, mineral exploration. ISPRA is currently involved in PanAfGeo in the coordination of the WP-F Georesources Governance & OAGS/GSOs Institutional Strengthening and also actively involved in WP-E Geohazards and Environmental Management of Mines in cooperation with LTG (leader), Council for Geosciences-South Africa (co-leader), PGI, GeoZS in the organization of 6 technical training sessions in several African countries.


Another Italian contribution to GEOSS, namely to AfriGEOSS, is represented by the EC Project PanAfGeo (Phase II) PanAfGeo - Pan-African Support to the EuroGeoSurveys-Organisation of African Geological Surveys (EGS-OAGS Partnership), co-funded by DG-DEVCO, is a project which supports the training of geoscientific staff from African Geological Surveys through the development of an innovative training programme. The project aims to increase African-owned geological knowledge and skills for sustainable mineral exploitation and related infrastructures, and natural disaster prevention and mitigation. Specifically, PanAfGeo enhances the capacity and role of African national Geological Surveys; • Contributing to mineral resource assessments by national Geological Surveys in Africa; • Increasing the activity of national Geological Surveys in regional mapping and exploration to upgrade their geoscientific information base and mineral inventories; • Strengthening the level of geological knowledge and skills in national Geological Surveys through training; • Strengthening OAGS’ potential to meet the needs of the African continent. Capacity building is addressed to over 1,200 trainees (mostly African geologists) with the organization of 49 short- and medium-term trainings in several African countries focused on wide range of geosciences topics such as satellite imagery analysis, geological mapping through GIS techniques, geo-hazards geochemistry and analytical chemistry, economic geology, mineral exploration. ISPRA is currently involved in PanAfGeo in the coordination of the WP-F Georesources Governance & OAGS/GSOs Institutional Strengthening and also actively involved in WP-E Geohazards and Environmental Management of Mines in cooperation with LTG (leader), Council for Geosciences-South Africa (co-leader), PGI, GeoZS in the organization of 6 technical training sessions in several African countries.


The Paris Agreement is one of the three GEO Engagement Priorities. To achieve its targets, systematic and long-term earth observation data are needed, in order to improve carbon budgets, reduce uncertainties of national inventories, and provide decision makers with reliable information. Italy, through CMCC, is supporting by co-chiaring the GEO Working group on climate change (as chair of the Sub-group 3 on Mitigation 2020-2022) that is aimed to develop and implement a comprehensive GEO climate change action strategy to advance the use of Earth observations in support of climate adaptation and mitigation. Furthermore, through a dedicated activity within EU funded project (VERIFY and CoCO2), CMCC (Italy) is engaged in creating the links between the observation-based system for monitoring and verification of greenhouse gases foreseen by the project and GEO, ensuring the coordination with global data synthesis efforts.


A private sector perspective: Downstream services by e-GEOS e-GEOS, an ASI (20%) / Telespazio (80%) company, , is a Global Leader in providing high technologic and innovative geoinformation services and platforms based on Artificial Intelligence and cloud technology with digital, fast and customized access covering all fields of the Geo-Spatial Information business. CLEOS, e-GEOS latest launch, is the Information cloud platform to unlock geoinformation value in AI-powered applications accessible through an enhanced user experience offering a direct market place access to customized products. e-GEOS offers a unique portfolio of application services, from data acquisition to the generation of analytics reports, also thanks to its radar capabilities and to the fast access to the superior monitoring capabilities of the COSMO-SkyMed constellation of first and second generation. e-GEOS has acquired also a leading position within the European Copernicus Program. e-GEOS application platforms include experienced and solid services for environmental protection, rush mapping in support to natural disaster management, specialized products for defense and intelligence, oil spill and ship detection, maritime surveillance and security, assets and critical infrastructures monitoring, landslides and ground subsidence analysis, thematic mapping for agriculture and forestry, climate change phenomena monitoring.


EuroGEO Showcases: Applications Powered by Europe (e-shape) is aimed to implement a coordinated and comprehensive EO data exploitation initiative through collaboration amongst the European GEO Members and Participating Organizations in order to accelerate the users' uptake of open EO data and information for the benefit of Europe. The general objectives are to set-up and promote a sustainable organization dedicated to users' uptake of European EO resources, building on Copernicus and GEOSS through the development of co-design pilots (i.e. application-oriented products, services or solutions) built on a user-centric approach and delivering economic, social and policy value to European citizens. CNR with several Italian partners (CMCC, Fondazione CIMA, INGV, ISPRA, PLANETEK, UNICAL) is leading a Showcase on Health Surveillance with four Pilots: (EO-based surveillance of mercury pollution, EO-based surveillance of POPs pollution, EO-based pollution-health risks profiling in the urban environment and EarlY WArning System for Mosquito-Borne Diseases) and participates to Pilots on myEcosystem and Disasters Resilience Showcases.


Italy coordinates the LIFE NewLife4Drylands project (LIFE PRE/IT/000007; https://www.newlife4drylands.eu). It aims at the definition of a protocol for the use of Earth Observation to assess the effectiveness of Nature-Based-Solutions (NBS) for the restoration of degraded and desertified areas. NewLife4Drylands is coordinated by CNR (Institute of Atmospheric Pollution Research) and includes partners from Italy (CNR-Institute of Bioeconomy, ISPRA, University of Rome “La Sapienza”), Greece (Hellenic Society for the Protection of Nature, University of Crete) and Spain (CREAF). Restoration actions in six pilot sites in Greece (Nestos River, Mt. Asterousia), Italy (Palo Laziale, Alta Murgia) and Spain (El Bruc, Tifaracas) will be carried out for protocol design and evaluation. The protocol will consist of methodologies and best practices replicable and reusable on different contexts to support effective land management policies. The NewLife4Drylands protocol advances the use of remote-sensing and in-situ Earth Observation collected from disparate sources including GEOSS, as a resource for decision- making in land management applications. The protocol will be disseminated and exploited at national, European and global level including EuroGEO and GEO.


ERA-PLANET, the ‘European Network for Observing our Changing Planet’ (www.era- planet.eu), has been an ERANET Co-fund action under the EU Horizon 2020 framework programme, comprised of 35 partner organisations from 15 European countries, aiming at strengthening the European Research Area (ERA) in the domain of EO, in coherence with the European participation in the Group on Earth Observations (GEO) and the Copernicus programme of the European Union. Its goal was to bring together and strengthen the European, national and regional R&I programmes in the domain of EO, and develop a Transnational Environmental Observation System in support of European & international policies, through the integration of real- time monitoring data from various platforms, modelling tools and advanced global cyber- infrastructure for data sharing and interoperability. The four ERA-PLANET transnational projects were conclude on August 2021. More details at: SMURBS (www.smurbs.eu), GEO-Essential (www.geoessential.eu), IGOSP (www.igosp.eu) and iCUPE (www.atm.helsinki.fi/ icupe).


A private sector perspective: Planetek Italia is an Italian Benefit Company established in 1994, which employs 100+ women and men, passionate and skilled in Geoinformatics, Space solutions, and Earth science. Planetek provides solutions to exploit the value of geospatial data through all phases of data life cycle from acquisition, storage, management up to analysis and sharing. The company operates in many application areas ranging from environmental and land monitoring to open-government and smart cities, and including defence and security, as well as Space exploration and EO satellite missions. Among its main activity areas, the development of software for the satellite on-board data and image processing leads to the creation of a new business model called SpaceEdgeTM. SpaceEdgeTM is a new concept of satellite as-a-service powered by an Artificial Intelligence (AI) enhanced processing framework embarked on satellites, which makes available in- orbit payloads, resources, and services on-demand: services include EO data acquisition, processing, actionable information extraction, downlink, and distribution. Information detected in Space is then transferred back to the Ground as notifications and alerts or directly exploited on-board in autonomous decision workflows. Useless data and information non-relevant to the application’s workflow can be discarded, saving memory, bandwidth and thus increasing the efficiency and quality of automated pipelines too. The fields of application of on-board processing to reduce information latency are numerous, and will address GEO's priority engagement areas including the United Nations 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, the Paris Agreement, and the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction.


Italy is strengthening the coordination amongst national experts involved in Earth Observation (EO) domains through the GEO-ITALY Group (www.geoitaly.org). The GEO-ITALY overarching goal is to reinforce the synergies amongst involved research and university institutions as well as the private EO sector in Italy, thus facilitating a broad range of capacity building and outreaching activities to stakeholders and policy makers both at national and international level. Members of GEO-ITALY are Representatives of the Ministry of Universities and Research (MUR) and the Ministry of Environment and Energy Security (MASE) and scientists, researchers and managers employed in several Institutes of the National Research Council of Italy, in the National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology (INGV), in the Italian National Institute for Environmental Protection and Research (ISPRA), in many other public institutions in the Country, such as the Italian Space Agency (ASI) and the Euro-Mediterranean Centre on Climate Change (CMCC), as well as in private companies such as PLANETEK, Latitudo40, e-GEOS, just to cite a few.


The Global Observing System for Mercury (GOS4M) is a GEO Flagship with aim to foster the sharing of monitoring data and modelling tools to support the implementation of the Minamata convention on Mercury at various geographical scales. GOS4M (www.gos4m.org) is aimed to federate existing networks of monitoring programmes and observing infrastructures – currently it provides a link to the Global Mercury Observation System (GMOS – www.gmos.eu) and other major existing regional networks. During the last year GOS4M developed the Knowledge Hub aimed to support the achievement of the objectives of international programmes and conventions related to mercury pollution which include UNEP, Minamata Convention on Mercury (MCM) Secretariat, UNECE-LRTAP and 2030 UN Agenda on SD. Special attention is paid to support all interested Parties in the implementation of the MCM. To this end global comparable monitoring data, validated models and policy interoperable tools are provided as part of the GOS4M Knowledge Hub designed to evaluate the relationship between cause and impact of mercury contamination, analyse cost-effective strategies aiming to reduce the mercury contamination at regional and global scale and co-design policy scenarios aiming to achieve the target of the MCM. The GOS4M KH provides also a tool to estimate the investment costs associated to a given mitigation strategy as well as the possibility to evaluate the risk for human health associated to major exposure patterns of mercury contaminated environments and food. GOS4M is also contributing to the GEO Knowledge Hub.


Italy is continuing its activity aiming to improve discovery and access to data, information and knowledge and to support and further develop the GEOSS Platform as an open and public global infrastructure for data sharing and knowledge generation. Italy continues operating and advancing the GEO Discovery and Access Broker (GEO DAB) framework as one of the key components of the GEOSS Platform. Italy carries out activities for knowledge generation and management developing the Virtual Earth Laboratory (VLab), a knowledge platform for model sharing and running in multicloud environments. Italy is co-chair of the GEOSS Platform Operation Team (GPOT) and member of the GEO Infrastructure Development Task Team (GIDTT). It also participates to the activity of the GEO Data Working Group and its sub-groups. For the advancement and utilization of the GEOSS Platform, collaborations are ongoing with ESA, EC-JRC, USA (USGS), Germany (DWD), Switzerland (University of Geneva), China (Ministry of Science and Technology), Chile (Ministerio de Bienes Nacionales).

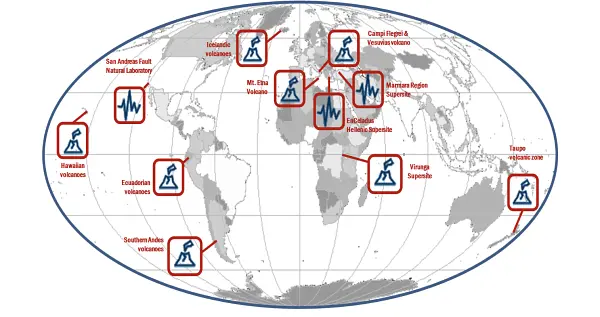
The Italian Space Agency (ASI) actively supports GEO Initiatives related to Disasters Risk Reduction like GEO-GSNL. ASI regularly provides thousands products from its national asssets (mainly COSMO- SlyMed, but also PRISMA and SAOCOM over ASI Area of Interest) to all the 13 Supersites and Natural laboratories all over the world and to pilot projects whose purpose is to demonstrate the value of earth observation data for Disaster Risk Reduction and to build regional capacity in this sector.


Italy, through the INGV, coordinates and supports with important in-kind resource, the GEO- Geohazard Supersites and Natural Laboratories initiative (GEO-GSNL), established in 2010 under the Disaster SBA. GSNL is a network of 11 Supersites where a large community of scientists works to generate products for science-based decision making in Disaster Risk Management. GSNL is supported by the CEOS space agencies with satellite imagery and by a number of local monitoring agencies with in situ data. Supersite scientists openly share their in-situ and satellite data, promoting an Open Science approach and focusing on the sharing of scientific knowledge, capacity development, and technological innovation to increase the societal benefit geohazard science. All the Supersite coordinators are authoritative actors in the national frameworks for disaster prevention and response, and as such they constantly deliver hazard information generated for the Supersite, to the national decision makers, ensuring rapid and direct societal benefit of scientific findings. The Italian Space Agency (ASI) also supports GEO-GSNL, providing, on a continuous basis, over 2500 COSMO-SkyMed products per year that are key for achieving the GSNL objectives.

The Italian Space Agency (ASI) has launched on 22 March 2019 the PRISMA satellite carrying an hyperspectral sensor with a Ground Sampling Distance (GSD) of 30 m and covering the wavelength range from 400 nm to 2500 nm, with 10 nm spectral sampling. The launch was successful and the in-orbit commissioning has been completed, allowing PRISMA data to be accessible since May 2020 through the dedicated portal https://prisma.asi.it/. Data policy is based on a quasi-open and free access, with limitations on products per user quantities and on priorities for acquisition requests conflicts solving, to cope with the operational capabilities of the mission. Data policy allows commercial exploitation of value added product/services still delivering free of charge but forbids PRISMA original data redistribution. PRISMA catalog is now visible through GEOSS.


The Italian National Copernicus User Forum reflects the procedure of the Copernicus User Forum. It is composed of representatives of user communities belonging to public institutions, public and private research bodies, industries and enterprises, covering all the Copernicus domains. Each User Community representative participating in the activities has to stimulate the community that represents, from central to local level, by promoting the use of Copernicus services and products and to link existing national EO initiatives.


Another Italian contribution to GEOSS, namely to AfriGEOSS, is represented by the EC Project PanAfGeo (Phase II) PanAfGeo - Pan-African Support to the EuroGeoSurveys-Organisation of African Geological Surveys (EGS-OAGS Partnership), co-funded by DG-DEVCO, is a project which supports the training of geoscientific staff from African Geological Surveys through the development of an innovative training programme. The project aims to increase African-owned geological knowledge and skills for sustainable mineral exploitation and related infrastructures, and natural disaster prevention and mitigation. Specifically, PanAfGeo enhances the capacity and role of African national Geological Surveys; ● Contributing to mineral resource assessments by national Geological Surveys in Africa; ● Increasing the activity of national Geological Surveys in regional mapping and exploration to upgrade their geoscientific information base and mineral inventories; ● Strengthening the level of geological knowledge and skills in national Geological Surveys through training; ● Strengthening OAGS’ potential to meet the needs of the African continent. Capacity building is addressed to over 1,200 trainees (mostly African geologists) with the organization of 49 short- and medium-term trainings in several African countries focused on wide range of geosciences topics such as satellite imagery analysis, geological mapping through GIS techniques, geo- hazards geochemistry and analytical chemistry, economic geology, mineral exploration. ISPRA is currently involved in PanAfGeo in WP-D New Frontiers in Geosciences (Geoheritage and Geothermal energy)and WP-E Geohazards and Environmental Management of Mines in cooperation with LTG (leader), Council for Geosciences-South Africa (co-leader), PGI, GeoZS in the organization of 6 technical training sessions in several African countries. More details of th project in: https:// panafgeo.eurogeosurveys.org


Italy is part of the EuroGEOSec project consortium, which is aimed to support the EuroGEO vision and to prepare the transition of the EuroGEO initiative into a sustainable endeavor, by setting-up a EuroGEO secretariat. The overarching goal of the EuroGEOSec project is to support the coordination of the EuroGEO initiative and develop a sustainability plan guiding its long-term operation. This will be achieved by establishing the EuroGEO Secretariat with the mission to (i) strengthen GEO-related coordination mechanisms at European and national levels, (ii) support increased innovation, space application development and reinforcement of the European space data ecosystem concept; (iii) foster international cooperation to help stimulate the market and promote European technology and services; (iv) contribute to the European Green Deal objectives and the European strategy for data (EU Data Spaces) by further deploying and exploiting the use of EO towards a strengthened Global Earth Observation System of Systems (GEOSS).

Italy is participating to the construction of the EIRENE RI (Research Infrastructure for EnvIRonmental Exposure assessmeNt in Europe), an ESFRI (European Strategy Forum on Research Infrastructures) infrastructure, which fills the gap in the European infrastructural landscape and pioneers the first EU infrastructure on human exposome (environmental determinants of health). A starting point in the roadmap is the EIRENE PPP project that aims to prepare the implementation of EIRENE RI as a consolidated European research infrastructure enabling the development of advanced technologies and complementary services on the characterization of complex environmental exposures and their impact on the European population. This will promote European excellence in Environmental & Health research by providing European researchers with transnational and/or virtual access to harmonized capacities, unique services, and comprehensive data addressing the current and future needs of public authorities. The initiative will foster the GEO Health CoP.


Italy coordinates the LIFE NewLife4Drylands project (LIFE PRE/IT/000007; https://www.newlife4drylands.eu). It aims at the definition of a protocol for the use of Earth Observation to assess the effectiveness of Nature-Based-Solutions (NBS) for the restoration of degraded and desertified areas. NewLife4Drylands is coordinated by CNR (Institute of Atmospheric Pollution Research) and includes partners from Italy (CNR-Institute of Bioeconomy, ISPRA, University of Rome 'La Sapienza'), Greece (Hellenic Society for the Protection of Nature, University of Crete) and Spain (CREAF). Six case studies in Greece (Nestos River, Mt. Asterousia), Italy (Palo Laziale, Alta Murgia) and Spain (El Bruc, Tifaracas) will guide the design of the r protocol design. The protocol will consist of methodologies and best practices replicable and reusable on different contexts to support effective land management policies. The NewLife4Drylands protocol advances the use of remote-sensing and in-situ Earth Observation collected from disparate sources including GEOSS, as a resource for decision-making in land management applications. The protocol will be disseminated and exploited at national, European and global level including EuroGEO and GEO.


Italy is supporting the GEO and UN-Habitat 'Earth Observation Toolkit for Sustainable Cities and Human Settlements' Programme. The Programme participates in the EO4SDG Initiative and aims at developing a customizable and continually updated toolkit on the integration of Earth Observation and geospatial information into the urban monitoring and reporting processes on SDG targets and indicators based on inputs from UN Member States and cities. The CNR-IIA indicator estimation approach consists of deriving and updating, from Earth Observation data, some essential variables for the urban ecosystem: the spatial distribution and density of urban population and settlement maps. By integrating these essential variables with other domain-specific information i.e., the particle pollutant maps, specific urban resilience indicators and sub-indicators can be quantified. The case study focuses on updating the distribution map of the migrant population regularly residing in Bari and neighbouring municipalities to monitor progress on the inclusiveness and sustainable urbanization targets of the SDG 11 of the UN 2030 Agenda.


e-GEOS, an ASI (20%) / Telespazio (80%) company, , is a Global Leader in providing high technologic and innovative geoinformation services and platforms based on Artificial Intelligence and cloud technology with digital, fast and customized access covering all fields of the Geo-Spatial Information business. CLEOS, e-GEOS latest launch, is the Information cloud platform to unlock geoinformation value in AI-powered applications accessible through an enhanced user experience offering a direct market place access to customized products. e-GEOS offers a unique portfolio of application services, from data acquisition to the generation of analytics reports, also thanks to its radar capabilities and to the fast access to the superior monitoring capabilities of the COSMO-SkyMed constellation of first and second generation. e-GEOS has acquired also a leading position within the European Copernicus Program. e-GEOS application platforms include experienced and solid services for environmental protection, rush mapping in support to natural disaster management, specialized products for defense and intelligence, oil spill and ship detection, maritime surveillance and security, assets and critical infrastructures monitoring, landslides and ground subsidence analysis, thematic mapping for agriculture and forestry, climate change phenomena monitoring.


A further contribution of Italy to the many GEOSS Ecosystems tasks is offered by the GEO ECO (GEO Global Ecosystem) Community Activity and Action Group, co-lead by CNR. GEO ECO builds up and extends the approach used in the European Horizon 2020 ECOPOTENTIAL project, led by CNR, and from a few other initiatives, to other protected areas in Europe and in other continents. GEO ECO aims to use available Earth Observation data, research results and tools on a global scale for enhancing knowledge on natural ecosystems, identifying protected areas (PAs) of international relevance as focus areas for its activities, as they are aimed to preserve natural ecosystems, and thus have a high intrinsic value for human societies. In Italy, a key PA will be the Gran Paradiso and the Alta Murgia National Parks, also involved in ECOPOTENTIAL, the former H2020 project on Earth Observation data for ecosystems in protected areas supporting GEO (2015-2019). The detection and modelling of the state and development of natural ecosystems in PAs is a priority for the monitoring the advancement of the SDG 14 and 15. It also extends its analysis to unprotected areas. GEO ECO is adopting the view of ecosystems as 'one physical system' with their environment, characterized by strong geosphere-biosphere-anthroposphere interactions across multiple space and time scales.


Planetek Italia is an Italian Benefit Company established in 1994, which employs 100+ women and men, passionate and skilled in Geoinformatics, Space solutions, and Earth science. Planetek provides solutions to exploit the value of geospatial data through all phases of data life cycle from acquisition, storage, management up to analysis and sharing. The company operates in many application areas ranging from environmental and land monitoring to open-government and smart cities, and including defence and security, as well as Space exploration and EO satellite missions. Among its main activity areas, the development of software for the satellite on-board data and image processing leads to the creation of a new business model called SpaceEdgeTM. SpaceEdgeTM is a new concept of satellite as-a-service powered by an Artificial Intelligence (AI) enhanced processing framework embarked on satellites, which makes available in-orbit payloads, resources, and services on-demand: services include EO data acquisition, processing, actionable information extraction, downlink, and distribution. Information detected in Space is then transferred back to the Ground as notifications and alerts or directly exploited on-board in autonomous decision workflows. Useless data and information non-relevant to the application’s workflow can be discarded, saving memory, bandwidth and thus increasing the efficiency and quality of automated pipelines too. The fields of application of on-board processing to reduce information latency are numerous, and will address GEO's priority engagement areas including the United Nations 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, the Paris Agreement, and the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction.


Latitudo 40 is a startup founded by four deep tech and space experts in 2017, which now employs a team of more than 15 people, with a predominance of Data Science experts for the development of new algorithms based on AI/ML and generative AI applied to the analysis and understanding of multi-spectral and hyperspectral satellite imagery. Latitudo 40, to make the most of the value of geospatial data, has invested in the development of a cloud-based platform to be used in SaaS mode for the analysis and monitoring of urban environments, with particular reference to the issue of planning sustainable and resilient cities of the future, identifying the main risks for the population and infrastructures (urban heat islands, urban heat risks, floods) and creating a map of intervention priorities for public decision-makers and urban planners, indicating possible mitigation actions using Nature Base Solutions. In addition, Latitudo 40 has developed a dataspace from space to foster the adoption of Geospatial solutions. In this space, system integrators and developers can find always-available datasets to understand urban risks better and create new applications in city monitoring, precision agriculture and infrastructure monitoring. EarthDataPlace makes spatial datasets available to everyone easily, quickly and inexpensively. Latitudo 40 supports the market with a vision of 'learning from the past, monitoring the present and designing the sustainable place of the future', and to pursue this strategy, it has launched its Place Simulator. This environmental scenario simulator takes as 'input' the different options for modifying the environmental scenario (changes in land cover/land use, new trees or green areas, etc.). It generates as 'output' synthetic satellite images obtained with Generative AI to assess the impact of the different scenarios and identify the best solution for the environment. The application areas of Latitudo 40 solutions provide a better and more detailed understanding of the variables that affect our environment and predominantly impact GEO's priority areas of endeavor, including the UN 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, the Paris Agreement and the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction.

